Examples of Expand Dataset Data
Example 1: Style to Style Size
A simple example is expanding with a single key. You can expand from Style to Style / Colour.
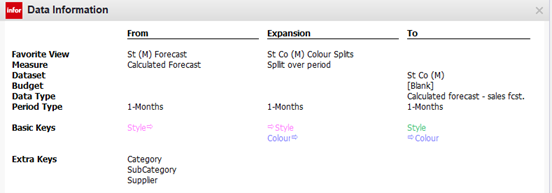
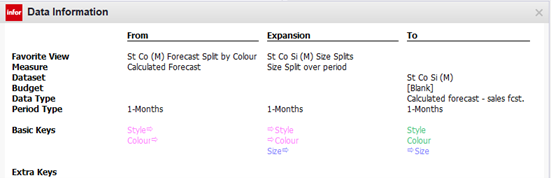
A second expansion then extends from Style / Colour to Style / Colour / Size.
Example 2: Style to Item number
In this example, the forecast is generated at the Style level. The Expansion view defines how the forecast is distributed to individual Item Numbers based on Size, Width, and Package.
The Style, identified as UCHDPR, represents a combination of model, material, and color.
The DMP operation generates the dataset of Item Numbers and Warehouses required by M3 BE to accept the forecast.
Each Item Number is constructed by combining the keys from the From view and the Expansion view in this format:
[Style][Size][Width][Pack]
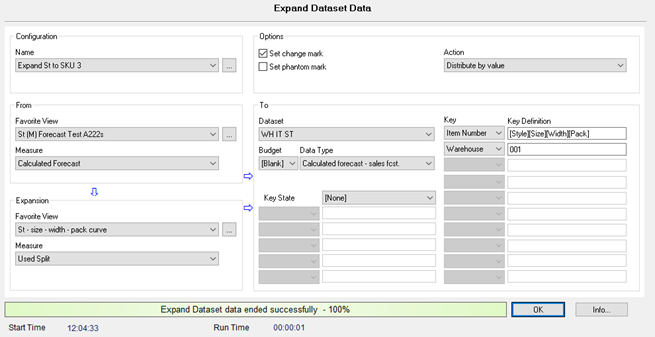
The Data Information dialog box shows that Style is being matched in the two views. The Style and Style Template are copied along with the generated Warehouse and Item Number.
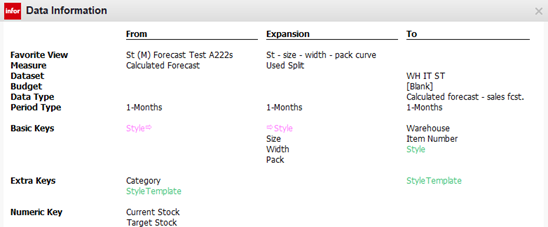
Each Style needs to have an expansion defined in the Expansion view. If missing, DMP skips the records and logs that they were skipped.
Example 3: Expansion by template
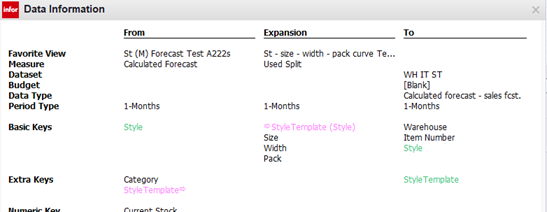
Alternatively, you can use a template to make maintenance easier. The setup is almost identical to example 2, but the expansion is defined by a key named .
In the From view, is defined as an extra key, and a value is assigned for each style to determine which template the expansion uses.
Example 4: Style / Warehouse to SKU Warehouse
The Style key and Warehouse are used as template keys, so they are present in both the From and Expansion views, as well as in the To Dataset. This allows DMP to properly filter and update the To Dataset. The From view is aggregated to Style / Warehouse.
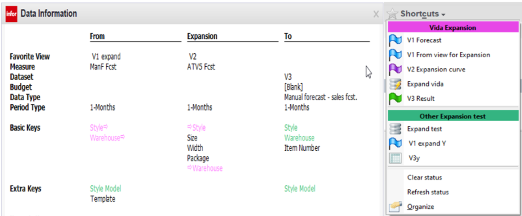
- From view aggregated for expansion

- From view all data with no aggregation
If this view was used as From view, then a red arrow is displayed because not all the basic keys are matched. You can notice the red arrow and the red border around the button.

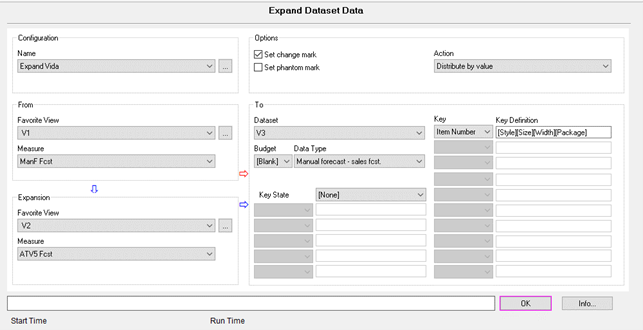
- Expansion view
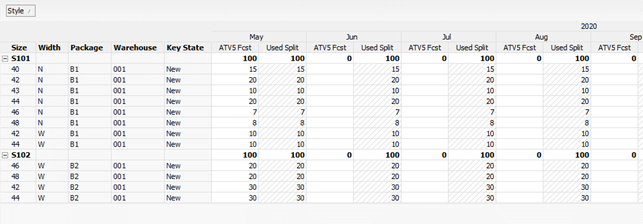
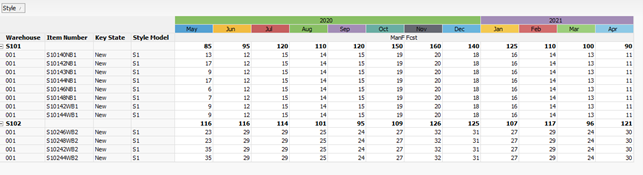
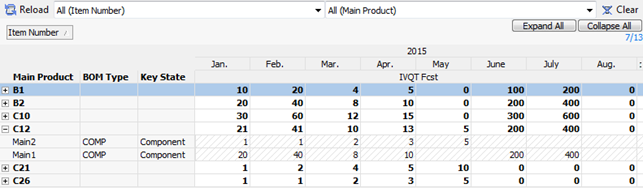
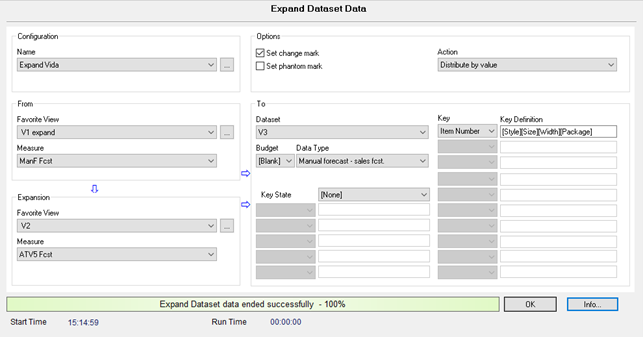
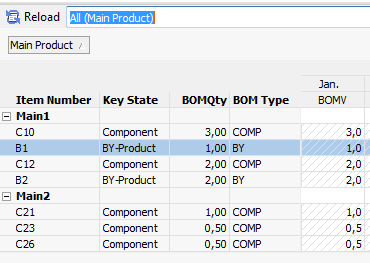
Example 5: Component expansion from Bill of Material
This example assumes a fixed quantity in the BOM:
- From view: Main Product
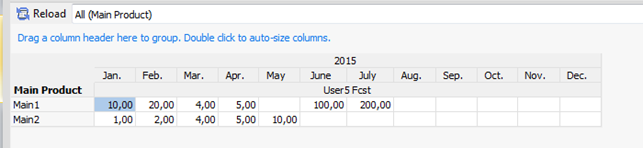
- Expansion view: BOM
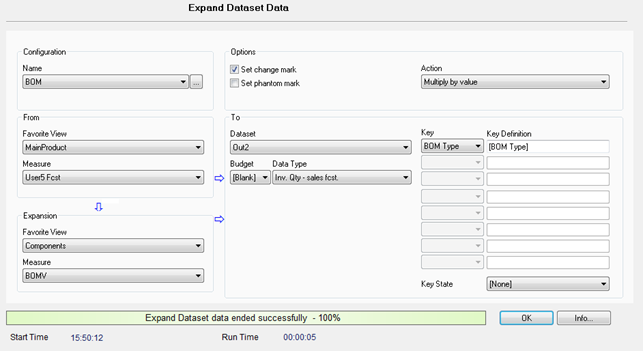
- Run the expansion. is the
selected action.
- To Dataset: Result
The quantity of components needed and the by-products output is calculated, and you can group them by individual components.