Adaptive Exponential Smoothing
Adaptive Exponential Smoothing is similar to basic exponential smoothing where the latest base demand value is weighted with a smoothing constant. In adaptive exponential smoothing, the smoothing constant is calculated every time a new forecast is made.
The smoothing constant is recalculated using this equation:
In order to control and follow up forecast precision, two types of measurements are used, and . These measure the deviation between forecast and actual demand. You can calculate the Mean Error and MAD in three ways:
Method 1: Exponential Smoothing
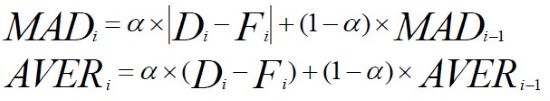
Method 2: Mean F/C deviation
Method 3: Mean Demand deviation
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Mean absolute deviation for period (i) | |
| α | Smoothing constant for exponential smoothing in period (i) |
|
|
The absolute amount of a difference (without minus sign) |
|
|
Base demand during period (i) |
|
|
Base forecast for period (i) |
|
|
Average demand for (n) periods |
| i | Period number |
| n | Number of periods included in calculating the mean |
Note: is
adaptive and calculated automatically from the deviation (CDev).