Example 1
In these examples, we will use time reporting to restructure data in different ways.
This is the structure of the input data:
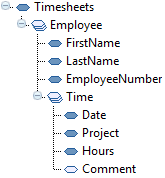
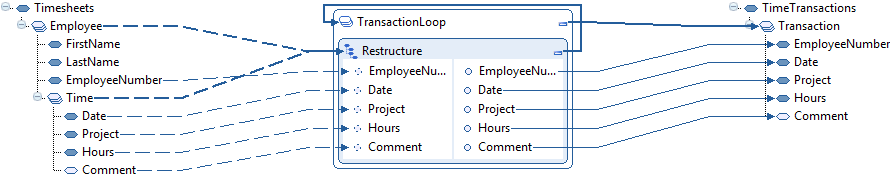
In this example, we want the time transactions in a flat structure:
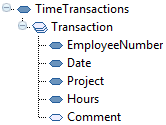
This can be done using manually created standard Java code in Java functions. Although, the task can be complicated and technically advanced. This is true if the output document requires a lot of nested loops with grouping and maybe summing, as in our next examples. The mapping will be cluttered with "technical" functions such as "AddToRecord", "AddToArray", "SortArray", "CheckBreak", and "GetFromArray".
The Restructure function does all these without the need for the user to create a single line of Java code. At runtime, all the processing is completed in a similar but more complex way. It is similar to solving the problem with a manually created Java code in the mapping.
See The Restructure Function topic in Restructure concepts.
- Create loops.
- We need to loop through all time transactions
to create the repetitive Transaction element in the output
document. Start by creating a loop that controls the output element Transaction.
See Defining Output data topic in Restructure concepts.
- Because we want to restructure the input data, we also insert a Restructure function in the loop. It will automatically control the loop.
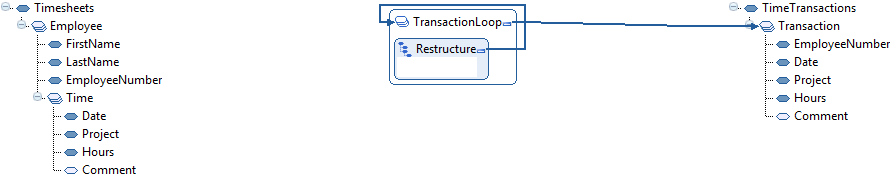
- We need to loop through all time transactions
to create the repetitive Transaction element in the output
document. Start by creating a loop that controls the output element Transaction.
- Select data.
- Drag and drop all data elements we want to use from the input document
to the Restructure function.
See "Defining Input Data" topic in Restructure concepts.
At this stage, we do not need to think about the repeating elements in the input document.
- Link the corresponding output parameters to the output document.
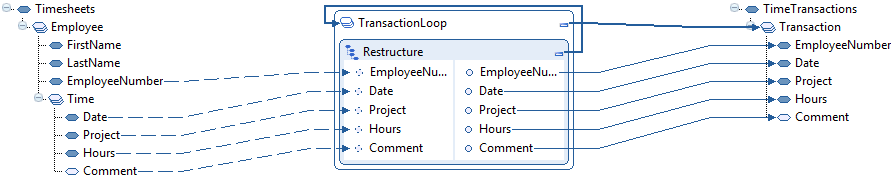
- Drag and drop all data elements we want to use from the input document
to the Restructure function.
- Select input loop levels.
Now, we need to "tell" the Restructure function which repeating elements in the input document we want to loop on when reading the input data.
In this case, this is what we want to do:
-
Loop on Employee, because we want data for all employees.
-
Loop on Time, because we want data for all time transactions per employee.
This table shows the movement for the elements:
Element Movement both Employee and Time -
from the input document
-
to the Restructure function’s header.
-
- Sort the data.
To restructure the data, we need to sort it and decide the sorting sequence.
For more information on sorting, see the "Sorting" topic in Restructure concepts.
To sort, set the property Sorting Sequence for the input parameters.
Follow this sorting sequence for the input parameter:
Input Parameter Sorting Sequence EmployeeNumber 1 Date 2 Project 3 - Complete the procedure.
Perform the final procedures such as:
-
Save the mapping to the mapper database.
-
Publish the mapping.
-
Set up an agreement.
-
Other required procedures, then test the mapping.
-