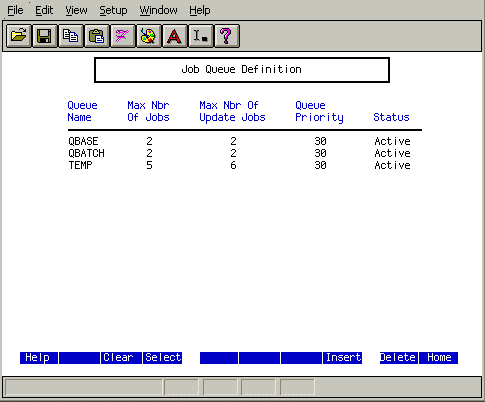
Defining a Job Queue
You can use the Job Queue Definition utility (jqdef) to define up to 100 job queues for running batch jobs. These queues are in addition to the default queue available initially after you install Lawson. Having additional queues is useful to assign different priorities to different queues and to balance the load on the system.
Before you define a job queue in the Job Queue Definition utility, you must first define the job queue on the IBM i system.
To define a job queue