Master Data Setup (PM)
Before you start to use the Preventive Maintenance (Service Planning and Concepts) module, you must set up or check some static data. This process includes checking planning parameters, defining measurement types, and defining activity groups.
Planning and Concepts setup sessions
Enter the Planning and Concepts data in the following sessions:
- Set planning parameters in the Service Planning Parameters (tsspc0100m000) session.
- Define units of measure in the Measurement Units (tsmdm0160m000) session.
- Define measurement types in the Measurement Types (tsmdm0165m000) session.
- Define activity groups in the Activity Groups (tsacm0110m000) session.
- Define usage classes in the Usage Classes (tsspc0130m000) session.
The following sections describe each of these sessions.
Service Planning and Concepts Parameters (tsspc0100m000)
Use the Service Planning Parameters (tsspc0100m000) session to check the default settings, because the time units are used in Planning and Concepts (SPC). If you intend to use counter-value maintenance or condition-based maintenance, make sure the Use Measurements check box is selected. If this check box is not selected, only usage maintenance is valid.
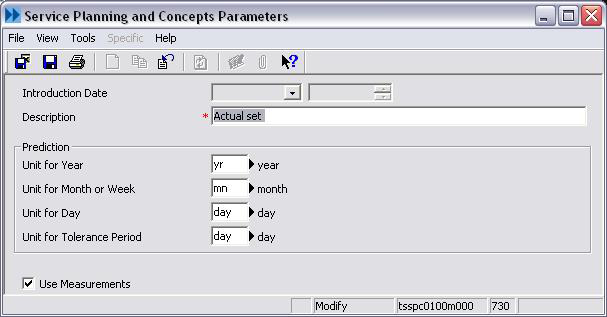
- Determine the time units that are appropriate to your planning requirements
- Make sure that the required time units and their conversions are entered into the logistic tables of LN Common Data.
Measurement Units (tsmdm0160m000)
Use the session to define units of measurement that counters can use to plan maintenance activity.
Measurements (tsmdm0165m000)
The counter value and the condition-based maintenance policies depend on the use of measurement types. Measurement types define the way in which a measurement is carried out. Characteristics used to define a measurement type include:
- An independent variable.
- A dependent variable.
- A norm value.
Example
The copier needs service at 15,000 copies, and you must estimate the time (independent variable) before a copier reaches that 15,000 level (dependent variable). If you link a measurement type to an item, the measurement type specifies that counter value maintenance must be performed. If you link a measurement type to a reference activity, you will perform periodic inspection maintenance.
Activity Groups (tsacm0110m000)
Use this session to define activity groups. Reference activities that are similar can be assigned to a common group. Assigning activities enables you to plan for the activity group rather than including multiple single activities in a maintenance plan.
Usage Classes (tsspc0130m000)
A usage class is a categorization of usage based on environmental factors. You can use usage classes to define more than one maintenance concept for an object or a model.
Example
The usage class of a truck can be national or international. The required maintenance for national use will be different than for international use.