Il seguente esempio illustra una distinta base multilivello.
|
Articolo prodotto: Bicicletta
|
|
Livello
|
Posizione
|
Articolo
|
Descrizione
|
Quantità
|
|
1
|
10 / 1
|
B
|
Sella
|
1
|
|
1
|
20 / 1
|
C
|
Telaio
|
1
|
|
1
|
30 / 1
|
D
|
Ruota
|
2
|
|
2
|
10 / 1
|
E
|
Raggi
|
35
|
|
2
|
20 / 1
|
F
|
Mozzo
|
1
|

| A | Articolo prodotto bicicletta |
| B | Componente acquistato sella |
| C | Componente acquistato telaio |
| D | Componente prodotto ruota |
| E | Raggi |
| F | Mozzo |
L'articolo prodotto D (ruota) è un articolo fantasma.
Il seguente esempio illustra una distinta base multilivello Utilizzo.
|
Articolo: Raggio
|
|
A livello di articolo
|
Articolo prodotto raggio
|
Posizione
|
Descrizione
|
Quantità
|
|
1
|
B1
|
20/1
|
Ruota anteriore
|
30
|
|
2
|
M1
|
30/1
|
City bike uomo
|
60
|
|
2
|
M2
|
60/1
|
Tandem donna
|
60
|
|
2
|
M3
|
70/1
|
Tandem uomo
|
60
|
|
2
|
M4
|
60/1
|
Tandem famiglia
|
60
|
|
1
|
B2
|
20/1
|
Ruota posteriore
|
30
|
|
2
|
M1
|
30/1
|
City bike uomo
|
60
|
|
2
|
M2
|
60/1
|
Tandem donna
|
60
|
|
2
|
M3
|
70/1
|
Tandem uomo
|
60
|
|
2
|
M4
|
60/1
|
Tandem famiglia
|
60
|
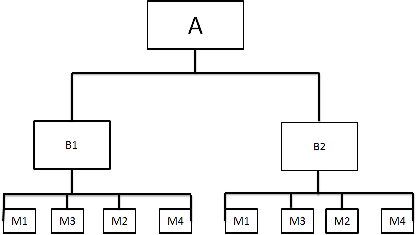
| A | Componente acquistato raggio |
| B1 | Ruota anteriore |
| B2 | Ruota posteriore |
| M1 | Articolo prodotto city bike |
| M2 | Articolo prodotto tandem donna |
| M3 | Articolo prodotto tandem uomo |
| M4 | Articolo prodotto tandem famiglia |
