Table definitions
Table Definitions define a structure to the data. The table code and name are attributes of a table. A table is a collection of data, arranged in rows (records) and columns (fields).
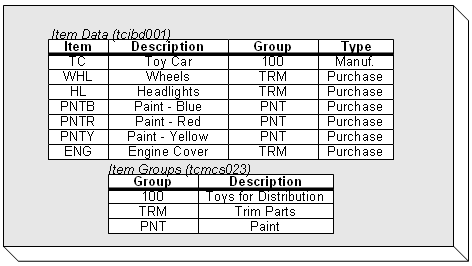
This diagram shows a table data example:
Fields, domains and indices
A table has fields. Table fields store individual pieces of data such as a customer name, the quantity of an item ordered, or the date a journal entry was made.
Table fields are linked to domains. Domains are components that define common information about data such as the following:
- The data type, such as a character type for customer name, a number type for quantity, and a date type for journal date
- Valid ranges
- Special characteristics such as capitalization rules
Domains ensure consistent data types for similar table fields.
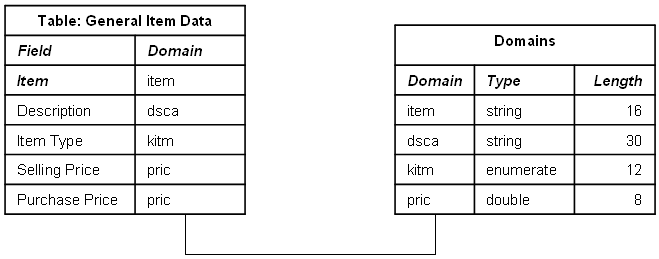
This diagram shows a table fields and domains example:
A table must have at least one index. An index consists of one or more table fields used to sort and search records in the table. The first index is always the Primary key, the unique identification for a record in a table.
Related Tables and References
The table may have a related table. A related table means that a field in the table refers to the key field of another table. Therefore, data can have relationships: customers can have orders; inventory stores items in warehouses; and employees work in a department. To create diagrams from these defined relationships, use a tool in the Enterprise Modeler.
Creating table definitions
Create table definitions in the Create a New Infor LN Software Component wizard and the Table Editor.
See Creating a table.