Hardware configurations
Stand-alone mode refers to a configuration where all components of the LN architecture run on a single machine. In stand-alone mode, an end user can work from the host machine or from a thin client machine. This is still possible, but not commonly used anymore.
The stand-alone mode configuration is shown in this diagram.
In a client/server configuration, the components of the LN architecture are distributed over two or more machines. There are many client/server configurations. The most common configurations are described here.
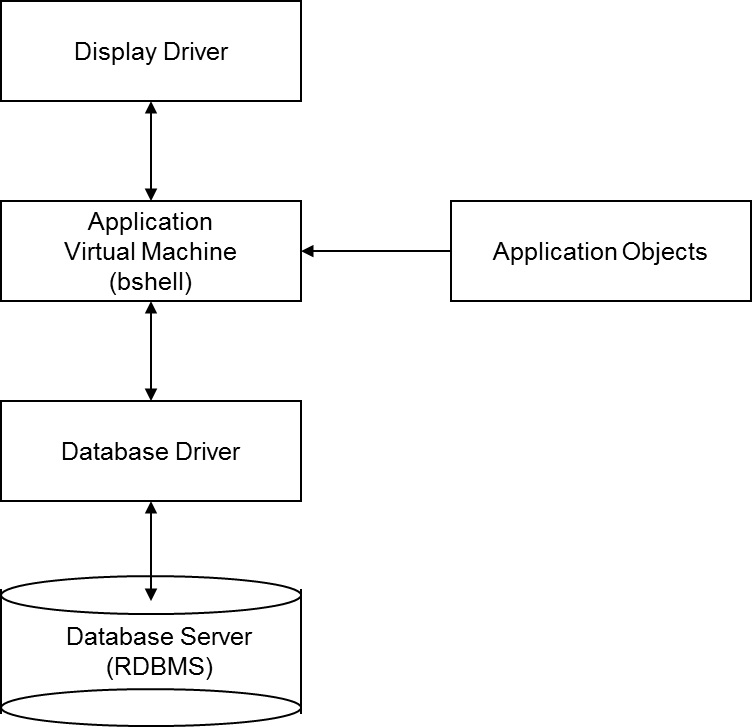
A straightforward client/server configuration is a variation of the stand-alone mode. In this configuration, the application tier, database driver and RDBMS are on one machine, but the display drivers are distributed among the user workstations. An instance of the application virtual machine and at least one instance of the database driver is started for each user. All users have access to the same application objects and database servers.
This diagram shows a variation of the stand-alone mode configuration:
When two machines are available as servers, two configurations are commonly used. In both configurations, the display drivers reside on the user workstations.
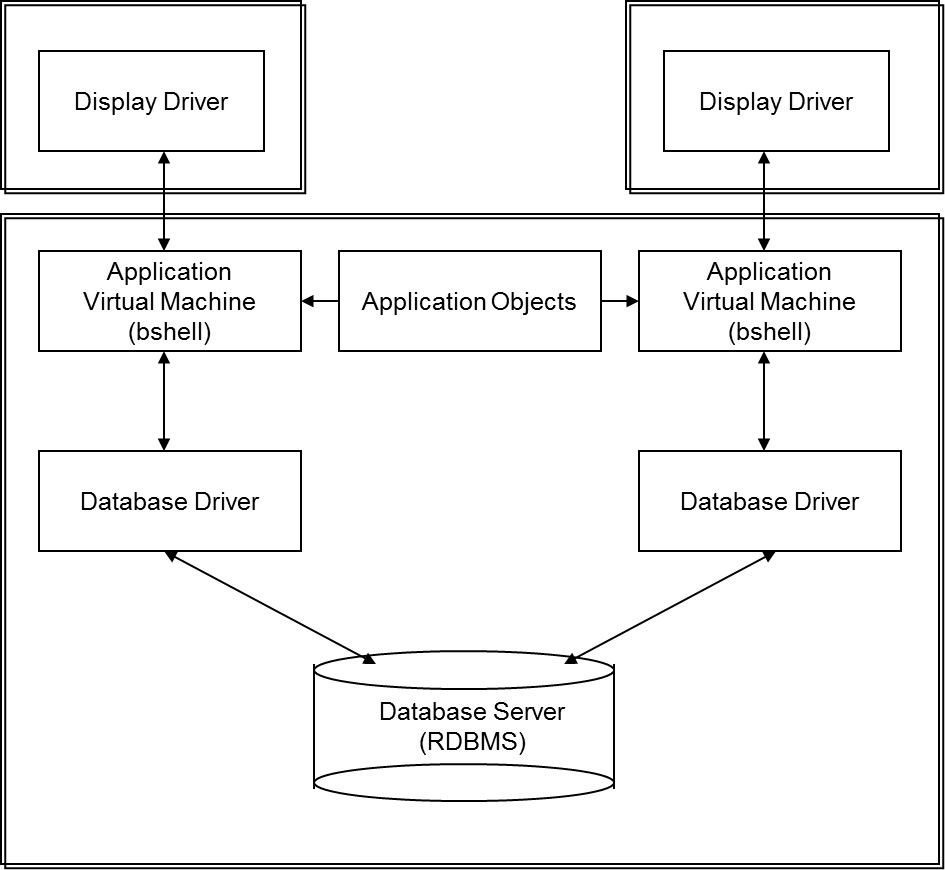
In the first configuration, the application tier and database driver are placed on one server, but the database server is placed on another. An instance of the application virtual machine and at least one instance of the database driver is started for each user. All users have access to the same application objects and database servers. This configuration uses the LN method of client/server access between the application virtual machine and the database driver.
This configuration is also know as 2-tier or host-mode configuration and is shown in this diagram:
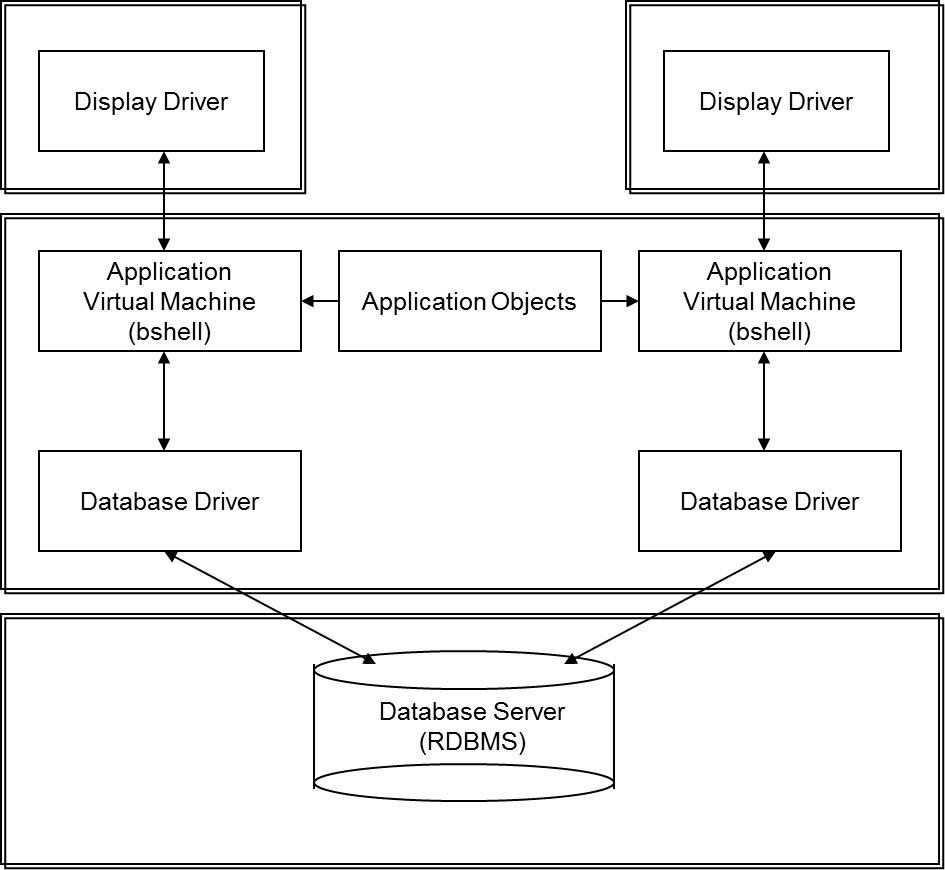
In the second configuration, the application tier is placed on one server, but the database driver and database server are placed on another. Like the previous configuration, an instance of the application virtual machine and at least one instance of the database driver is started for each user. All users have access to the same application objects and database servers. This configuration uses the RDBMS’s networked client functionality to provide client/server access. This configuration is also known as 3-tier.
The 3-tier configuration is illustrated in this diagram:
There are many other configurations of client/server systems, including dividing the application logic among multiple servers or using multiple servers for distributing the database.