Role browser (OP)You can view the roles and sub roles in the role browser, which shows a graphical representation of the roles in a role tree. The role browser uses the display logic of the existing desktop browser to ensure a consistent interface across the various browsers in LN. The role tree represents a role with all its sub roles, which subsequently can also contain sub-roles. You can define the authorizations for the sub-roles in the same fashion as for the roles. In the role browser, you can double-click a role folder to view the sub-roles in the role. To start the Role Data (ttams2100m000) session, select a role or sub role, and on the Options menu, click Role Data. Enhanced AMS The Role browser is replaced by the Role Data (ttams4100m000) overview session and Role Data (ttams4600m000) details session. The notion of role tree is removed in Enhanced AMS, for example, there is no longer a hierarchy of roles. The information and next figure do not apply. Continue reading at User-related procedures. This figure shows an example of a role with sub-roles. The manager has a number of roles linked to the manager role. The manager has the manager’s authorizations, and the authorizations of the product architect, product consultant, and project leader, all of whom are defined in their respective roles. The project leader role also has additional sub-roles. The Role Browser shows all the manager’s authorizations from the manager’s role to the role of the lowest-ranked employee: 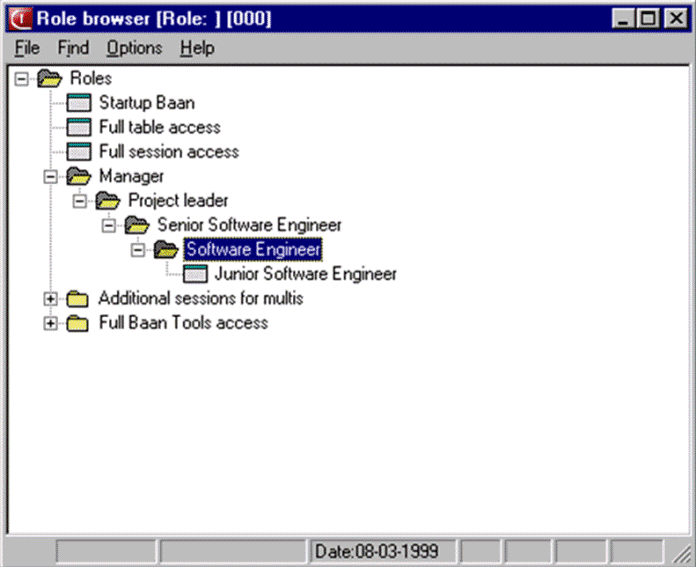 Role Browser You cannot define a recursive role structure. For example, a junior software engineer cannot have the authorizations of a senior software engineer in a sub-role. The Role Browser identifies and highlights recursive roles. You must delete the highlighted recursive roles. The following figure shows an example of a cyclical role. The junior software engineer also has the role of the senior software engineer, which of course is not the case: 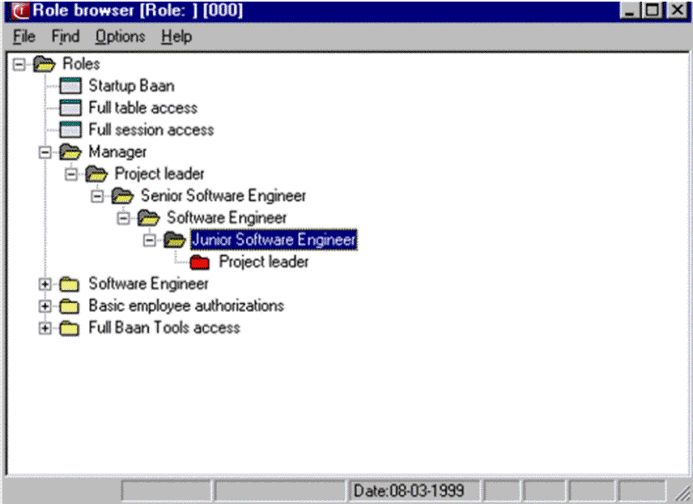 Example of a cyclical role
| |||