Event handlingIntroduction Event structure An event essentially consists of the following two parts:
If the data area is filled, which is not mandatory, one component will always have one or more attributes. In addition, this component can have child components. A typical example is a sales order object, in which the main component is the sales order and the child components are the order lines. The sales order component will have attributes such as order number, order date, and Sold-to business partner (customer). The order line component will have attributes such as line number, item, quantity, and price. Attributes can have old values, new (current) values, or both. Create events typically do not have old values, while delete events do not have new values. Change events can have either old or new values. Achtung! Although the logical structure of the events is stable, the technical format can change. The XSDs and XMLs in this chapter are included to illustrate the logical structure. For best results, use the event handling API, as described in "API for event handling" later in this chapter, when you use the contents of an event, because that interface must not change the event even though the XML structure can change. Beispiel The following figure illustrates the event used for a change, in this case, on a Customer object. Note that the component name, Customer, and the attributes are specific for this object. Other objects will have other values and can also have child components. Note, however, that events from Exchange will always be simple events, which are events that consist of only one component. 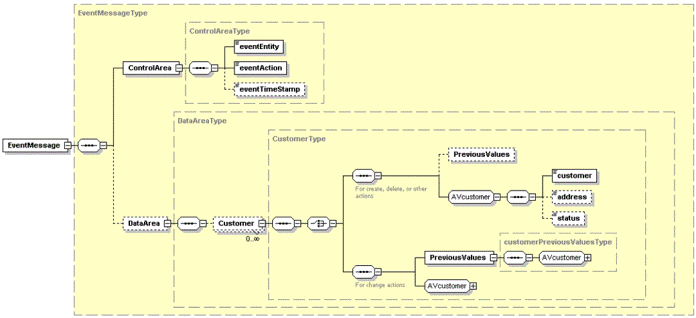 XSD for change event An XSD file for this structure contains the following code: <?xml version="1.0"?>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://www.baan.com" xmlns="http://www.baan.com" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="unqualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="EventMessage" type="EventMessageType"/>
<xs:complexType name="EventMessageType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ControlArea" type="ControlAreaType"/>
<xs:element name="DataArea" type="DataAreaType"
minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="ControlAreaType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="eventEntity" type="eventEntityDT"/>
<xs:element name="eventAction" type="eventActionDT"/>
<xs:element name="eventTimeStamp" type="eventTimeStampDT"
minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="eventEntityDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="eventActionDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="eventTimeStampDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:dateTime"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="DataAreaType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="Customer" type="CustomerType"
minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="CustomerType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:choice>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>For create, delete, or
other actions</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:element name="PreviousValues"
type="PreviousValuesEmpty" minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:group ref="AVcustomer"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>For change actions
</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:element name="PreviousValues"
type="customerPreviousValuesType"/>
<xs:group ref="AVcustomer"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:choice>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="actionType" type="eventActionDT"
use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="PreviousValuesEmpty"/>
<xs:complexType name="customerPreviousValuesType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="AVcustomer"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="identifierDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:group name="AVcustomer">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="customer" type="customerType"/>
<xs:element name="address" type="addressDT"
minOccurs="0"/>
<xs:element name="status" type="statusDT" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="customerType">
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="customerDT">
<xs:attribute name="identifier" type="identifierDT"
use="optional" fixed="true"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="customerDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:long">
<xs:totalDigits value="10"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="addressDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:maxLength value="9"/>
<xs:pattern value="\p{Lu}"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="statusDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:enumeration value="active"/>
<xs:enumeration value="inactive"/>
<xs:enumeration value="historic"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>The component names and attribute names in this XSD are dependent on the specific trigger. In this example, the component is Customer and the attributes are Customer, Address, and Status. The other parts are generic. The structure will be the same for all triggers. Note: The component class and attribute names will, in fact, be the ASCII files and ASCII file fields. Some examples of a change events based on this structure include the following: <EventMessage>
<ControlArea>
<eventEntity>customer</eventEntity>
<eventAction>create</eventAction>
<eventTimeStamp>2004-12-17T09:17:28Z</eventTimeStamp>
</ControlArea>
<DataArea>
<Customer actionType="create">
<customer>2147483647</customer>
<status>inactive</status>
</Customer>
</DataArea>
</EventMessage>
<EventMessage>
<ControlArea>
<eventEntity>customer</eventEntity>
<eventAction>change</eventAction>
<eventTimeStamp>2004-12-17T09:30:47Z</eventTimeStamp>
</ControlArea>
<DataArea>
<Customer actionType="change">
<PreviousValues>
<customer>2147483647</customer>
<status>inactive</status>
</PreviousValues>
<customer>2147483647</customer>
<status>active</status>
</Customer>
</DataArea>
</EventMessage>
<EventMessage>
<ControlArea>
<eventEntity>customer</eventEntity>
<eventAction>delete</eventAction>
<eventTimeStamp>2004-12-23T14:40:18Z</eventTimeStamp>
</ControlArea>
<DataArea>
<Customer actionType="delete">
<PreviousValues>
<customer>2147483647</customer>
<status>active</status>
</PreviousValues>
</Customer>
</DataArea>
</EventMessage>The "Examples" chapter provides additional examples. Events from Exchange Row events A row event generated from the Exchange module will always have one of the standard event types: create, change, or delete. In addition, the data area will only have one single component because only one table is involved. The ASCII file name is mapped to the component name in the event. The ASCII field names are mapped to the attribute names in the event. As a result, the example provided in "Introduction," previously in this chapter, is valid for events from Exchange, except that the component and attribute names will have a maximum of eight characters and will be lowercase. In addition, if you generate the exchange scheme as described in "To set up a trigger source" in Chapter 2, "To set up triggering," the ASCII file name, and consequently the component name, will be equal to the table code, while the ASCII field names, and consequently the attribute names, will be equal to the table field codes. End of Data Set event At the end of a batch line, an End of Set event is generated if an end of batch line trigger is defined in the export trigger. The following figure shows the event used at the end of an
export batch line: 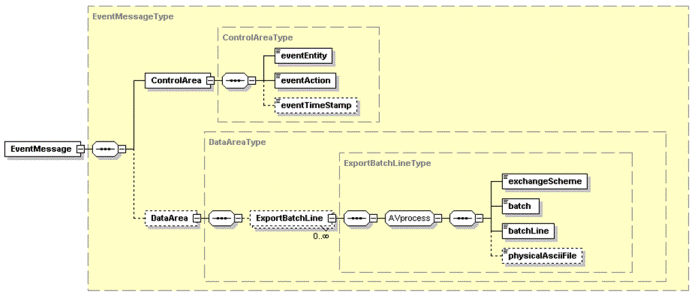 XSD for end of set event An XSD file for this structure contains the following code: <?xml version="1.0"?>
<xs:schema targetNamespace="http://www.baan.com" xmlns="http://www.baan.com" xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="unqualified" attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="EventMessage" type="EventMessageType"/>
<xs:complexType name="EventMessageType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ControlArea" type="ControlAreaType"/>
<xs:element name="DataArea" type="DataAreaType" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="ControlAreaType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="eventEntity" type="eventEntityDT"/>
<xs:element name="eventAction" type="eventActionDT"/>
<xs:element name="eventTimeStamp" type="eventTimeStampDT" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="eventEntityDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="eventActionDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="eventTimeStampDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:dateTime"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:complexType name="DataAreaType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="ExportBatchLine" type="ExportBatchLineType" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="ExportBatchLineType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:group ref="AVprocess"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="actionType" type="eventActionDT" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="identifierDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:boolean"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:group name="AVprocess">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="exchangeScheme" type="exchangeSchemeType"/>
<xs:element name="batch" type="batchType"/>
<xs:element name="batchLine" type="batchLineType"/>
<xs:element name="physicalAsciiFile" type="physicalAsciiFileDT" minOccurs="0"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:group>
<xs:complexType name="exchangeSchemeType">
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="exchangeSchemeDT">
<xs:attribute name="identifier" type="identifierDT" use="optional" fixed="true"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="batchType">
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="batchDT">
<xs:attribute name="identifier" type="identifierDT" use="optional" fixed="true"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="batchLineType">
<xs:simpleContent>
<xs:extension base="batchLineDT">
<xs:attribute name="identifier" type="identifierDT" use="optional" fixed="true"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:simpleContent>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:simpleType name="exchangeSchemeDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:maxLength value="8"/>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="batchDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="batchLineDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:long"/>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:simpleType name="physicalAsciiFileDT">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string"/>
</xs:simpleType>
</xs:schema>
An example of an end of set event based on this structure is as follows: <EventMessage>
<ControlArea>
<eventEntity>exportBatchLine</eventEntity>
<eventAction>endOfDataSet</eventAction>
</ControlArea>
<DataArea>
<ExportBatchLine actionType="endOfDataSet">
<exchangeScheme>workflow</exchangeScheme>
<batch>BATCH</batch>
<batchLine>1</batchLine>
<physicalAsciiFile>/home/workflow/export/customer.S
</physicalAsciiFile>
</ExportBatchLine>
</DataArea>
</EventMessage>
The physicalAsciiFile will not be set if no ASCII file is created. Additional examples are provided in Chapter 4, "Examples." API for event handling The implementation of the event handling API is stored in the datrgevent library. The library contains the following types of functions:
Achtung! To read events, you must only use the functions in the datrgevent library. The implementation can change. For details, refer to the specifications of the datrgevent library. Hinweis You can retrieve the library specifications from the library objects. At operating-system level, use explode6.2 to locate the library object, and subsequently use bic_info6.2 with the -eu options. For example:
This shows the documentation of the event handling functions. This method provides the following:
| |||