Glossary for Tools3GL script A program script that can be linked to sessions without
forms, or that is not linked to a session at all. 4GL statements and sections
cannot be used in 3GL scripts. In other words the entire program flow,
including the main function, needs to be specified. 4GL engine The program that provides default functionality for a session
to prevent application programmers from having to develop a session from
scratch. The 4GL engine, formerly called standard program (STP), is used
because essentially sessions are alike. In addition to providing default
functionality, the 4GL engine also provides a mechanism to change the 4GL
engine's default behavior, and to program dedicated functionality for a
specific session. Each time a session is started, a separate 4GL engine
instance is activated to handle the session. Synonym: standard program Acronym: STP 4GL script An event-oriented Program script that is linked to a session. The instructions can be specified in
program sections, form sections, field sections, main table input/output
sections, choice sections, zoom from sections, and functions. Active Directory Service Active Directory is an implementation of LDAP directory
services by Microsoft for use in Windows environments. Active Directory allows
administrators to assign enterprise wide policies, deploy programs to many
computers, and apply critical updates to an entire organization. An Active
Directory stores information and settings relating to an organization in a
central, organized, accessible database. Active Directory networks can vary
from a small installation with a few hundred objects, to a large installation
with millions of objects. Acronym: ADS additional file A generic component, such as an XML schema file, a GIF image,
and so on. From LN 6.0a
on, additional files are stored in a specific package, module, and package
VRC. ADS AFC algorithm A detailed finite sequence of actions that must be performed to
accomplish some task. AMS Application Foundation Classes Microsoft's Application Foundation Classes, a collection of
Java classes for creating full-fledged application programs. AFC is a
comprehensive set of Java class libraries providing user-interface controls,
graphics and effects classes, and the ability to create and extract cabinet
(CAB) files. Acronym: AFC application help Help that tells you how the application works. An online manual
contains an overview of the packages and the modules in each package and
explains the functionality of each module in detail, describing the underlying
concepts and applied methods. Application Programming Interface A set of methods that can be invoked by other applications. An
application's API enables other programs to retrieve data or to carry out
functionality from that application. Acronym: API Application Services Manager A stand-alone product that can start and stop LN application
services. Acronym: ASM appropriate menu Commands are distributed across the Views, References, and Actions menus, or displayed
as buttons. In previous LN and Web UI releases,
these commands are located in the Specific menu. array A list of data items of the same type with the same name. An
element in the array can be referenced by an expression composed of the array
name and an index expression. Multilevel arrays are used for data storage in
tables. ASM asynchronous communication Communication between processes, where the process that sends
the message does not expect, or wait, for a reply from the receiving
process. attachments Allows you to create or view documents that are attached to the
selected record. If you use object data management, you can attach documents to LN records such as items,
production orders, and service orders. attribute Literally, a characteristic. In databases, the name or
structure of a field is considered an attribute of a record. Structure refers
to its size and datatype. For example, LASTNAME, 50 characters, text. In screen
displays, additional information stored with each character in character mode
that controls the background and foreground colors of the character, blinking,
and underlining. audit To create an audit trail that traces all activities that affect
a piece of information, such as a data record, from the time it is entered into
the LN database to the
time it is removed. audit category A group of audit profiles, used to group audit profiles of the
same functional area. audit data dictionary A representation of the definition of an audited table in the
data dictionary at a certain point of time. When a sequence file is created,
the audit DD is kept in the sequence file's header. When the data dictionary
changes in a way that affects the table, a new sequence file is created and the
new audit DD is added. audit host The system where the audit server runs. audit management A management system that controls the auditing process. Audit
management can be used, for example, to specify for which database tables an
audit trail must be created and where the audit trail's data must be stored. audit profile A group of audit settings, configured for specific companies,
tables and fields. audit server A program that creates the audit trail. audit trail A means of tracing all activities affecting information, such
as data records in a database, for a defined time interval. The information is
stored in the audit files. audit type The setting that defines when a field is audited. You can choose to audit a field 'always', or only when it is 'changed':
Authorization Management System An authorization system in LN that defines the
permissions of a normal user. The user is assigned to a group of users with the
same role and/or sub role in an organization. LN links the
authorizations to the role of the user group, not to the individual users in
the group. Acronym: AMS authorizations A set of permissions that limit the access to various objects
in LN. For example, access
can be denied to sessions, tables, and companies. base language The fallback language that is used to display application data. LN uses the following fallback mechanism:
For more information, refer to Multilanguage application data. base VRC A means in PMC to identify products in a unique way. Updates at
the distributor side are provided with the base VRC identifier. A base VRC can
contain the code of the physical VRC in which the related master product is
installed, for example, B61_a, but can also be a code not related to a physical
VRC, for example, 7.6_a_tt. At the recipient side, every update VRC is linked
to a base VRC identifier. The installation process checks if the base VRC
identifier of the update matches with the base VRC identifier of the update
VRC. If not, you cannot install the update in that update VRC. base VRC combination A Base VRC combination is defined at the PMC distributor
side and consists of a set of related base VRCs. A base VRC combination
controls the creation of co-requisites between base VRCs. You can only define
co-requisites between base VRCs that are part of the same base VRC combination.
Base VRC combinations prevent the unwanted creation of co-requisites between
base VRCs. batch-oriented replication A time-driven data replication method, as opposed to the
real-time data replication. The batch-oriented replication process is started
based on a schedule, for example, every hour or every week. bi-directional language support A function that is necessary to support languages that are read
and written from right to left. For example, Arabic, and Hebrew. blocking process A process that must be completed before other processes can
continue. BOI BOL BOR BSE BSE path An environment variable containing the directory where the LN software is installed. bshell See: LN shell business object A business object is an object understandable by the business,
such as a purchase order or an organizational unit. A business object has
information stored in the business object attributes, such as the purchase
order number or the organizational unit name. A business object also contains a
set of actions, known as business object methods, that can manipulate the
business object attributes, such as create purchase order and list
organizational units. From a development perspective, a business object is a collection of tables and functions that manipulate these tables that are implemented simultaneously as one group during the development phase. A business object is identified by the combination of a package code, module code, and business object code. Business Object Interface Business Object Interfaces provide a connection between
partner applications and third-party applications and the LN software, as well as
connecting LN functional
components. Business Object Interfaces are developed for situations where the LN software acts
principally as a server, and a client software invokes the methods in the
objects. Acronym: BOI Business Object Layer A set of standard DLLs from LN 6.0 onwards. The
Business Object Layer invokes LN business logic methods that handle the persistency of
a Business Object Acronym: BOL business object meta data Describes the structure and content of a Business Object and
its mapping to LN tables
and DLLs. Business Object Repository A persistency system that stores the Business Object meta data. The BOR is a virtual space in which Business Objects are modeled. The
runtime objects of the business objects are stored in the Business Object Layer. Acronym: BOR BW See: LN windows
interface C A structured programming language. C is a compiled language
that contains a small set of built-in functions that are machine dependent. The
rest of the C functions are machine independent and are contained in libraries
that can be accessed from C programs. C programs are composed of one or more
functions defined by the programmer. character set The smallest component of a written language that has semantic
value (that is, linguistic meaning). A character set is the collection of
characters that is used in a given language. As well as the alphabet, a
character set includes numerals, mathematical and currency symbols and
punctuation marks. The character set that you select determines how texts are
displayed and printed by your computer, for example as Latin or Arabic
characters. Examples of character sets include ASCII and ISO 8859-1. chart A graphic or diagram that displays data or the relationships
between sets of data in pictorial rather than numeric form. The data can be
presented in a graph, a line, or a pie, and can include titles, legends, and
footnotes. chart application A program that is used to send data from a LN session to the Chart
Manager. A chart application is linked to a package VRC to customize the
attributes that are specified in the chart. chart type The chart type determines what the chart looks like. For example, it defines the type of graph, the thickness of lines, the size of bars, and the colors. The following default chart types are present in LN:
check in A process that releases the checked-out software component and
copies the software component from the Development VRC to
the Original VRC.
This process also stores a historical version. A revision text for the changed software component is required for a check-in process. check out A process that locks the software component for other
developers. During the check-out phase, other related components are locked as
well while the component can be updated and tested. A copy of the component is
made from the original VRC to the Development VRC. child field A table field that is part of a combined field. A combined
field contains two or more table fields, which are the child fields of the same
table field. class In object oriented programming, a class is a generalized
category that describes a group of more specific items, called objects, that
can exist within it. A class is a template definition of the methods and
properties (variables) in a particular kind of object. Thus, an object is a
specific instance of a class that contains real values instead of variables.
The class is one of the defining ideas of object-oriented programming. Among
the important ideas about classes are: A class can have subclasses that can
inherit all or some of the characteristics of the class. In relation to each
subclass, the class becomes the superclass. Subclasses can also define their
own methods and variables that are not part of their superclass. The structure
of a class and its subclasses is called the class hierarchy client A user, program or system that requests the execution of a
specific task from another program or system. See also server. client/server environment A distributed system in which software is split between server
tasks and client tasks. A client sends requests to a server, according to a
protocol, asking for information or action, and the server responds. collection In PMC, a collection is a group of individual solutions. At the
PMC distributor side, you can perform grouping in various ways, for example,
manual grouping based on a functional topic or grouping based on solutions
created in a particular period etc. You cannot define dependencies between
collections. At the recipient side, the entity collection is not available.
When a collection is scanned, the individual solutions are added to the PMC
registry and can be processed individually. combined field A combination of two or more child fields of the same Table. commercial product A set of tools, directories, or sessions which you can deliver
to a customer. commit An action to successfully complete a transaction in order to
make the database changes permanent. commit protocol An action to successfully complete a transaction in order to
make the database changes permanent. common user data The parts of the user data that are similar for a group of
users. The authorization data is not included in this definition. The user
authorizations are defined in the Authorization Management System. company A means to store data separately in LN. Every company has its
own tables with its own data. Example: An Item with Item Code "X" can be stored in the Item Master Table of several different companies. In each company this Item Code "X" can have different data. Note Company number 000 is reserved by Infor to store the Enterprise Server (Tools) data. Several company numbers below 100 are used by Infor as demo companies or base companies. Infor advises you to use only company numbers equal to or greater than 100 to store your production data. component management A system that a developer uses to lock software components,
that will be changed, for other users. co-requisite In general, co-requisites are defined between solutions of a
standard product and derived products. Co-requisites guarantee that related
products are updated simultaneously under the condition that the update VRCs of
the related products are linked to the same VRC combination. The order of
installation is not relevant. The solutions can have the same base VRC, or different base VRCs. customer A code that identifies a customized software package. For
example, B61O_a_cus1, where 'B61O' represents the version, 'a' represents the
release, and 'cus1' represents the customer extension of the customized
software. customization A derived product, meant to fulfill the requirements of a
specific customer or group of customers. da See: Data Director daemon A program associated with the UNIX operating system that
permanently runs in the background. A daemon handles requests that are issued
by other programs and is activated only when needed. For example, the job
daemon runs permanently on the LN server. If the job daemon detects that a job is
present, it executes the job at the job's scheduled time. DAL See: Data Access Layer Data Access Layer A Dynamic Link Library that is linked to a LN database
table. Acronym: DAL database A collection of data that is organized so that its contents can
easily be accessed, managed, and updated. A database has tools to search for
data in the database, sort the data in the database, and so on. database administrator The individual responsible for the installation, planning,
configuration, management control, and maintenance of the relational database. database authorizations The set of sessions that can be used to print, display,
maintain and convert the authorizations that a group of users with the same
role, has for specific tables and table fields in the database. database group A group of database users with the same authorizations and
rights. When you add a database user to a database group, the user
automatically receives the group's authorizations and rights. Database Management System A software interface between the database and the application
software. A database management system handles user requests for database
actions and allows for control of security and data integrity requirements. Acronym: DBMS database user An LN user
that is also authorized to access the database. The configuration information
for the database user contains all the necessary settings to log on to a
database. When the user logs on, these settings are automatically loaded. Every
database user must belong to a database group. Data Dictionary A database containing data about all the databases in a
database system. Data dictionaries store all the various schema and file
specifications and their locations. They also contain information about which
programs use which data and which users are interested in which reports. Acronym: DD Data Director The LN package that contains the Exchange module. Acronym: da data label Contains the name or the value of a data point. data language The language in which the application data is displayed. Data
languages can be linked to users and to software languages. A data language consists of an ISO 639-1 language code and, optionally, an ISO 3166-1 country code. data point A point in a chart that represents a value and is made visible
by means of a symbol, bar, pie segment, or a step in a line. The data point
value is determined by the chart series, the category, and the data value. data replication A method of table sharing in which every modification of a
table is copied to the companies that share the table. In LN, you can perform Batch-oriented replication by using the Exchange module. Synonym: replication Data Upgrade Engine A framework that executes application data upgrade programs. The Data Upgrade Engine is used after installation of a Feature Pack. Acronym: DUE data upgrade run The execution of multiple upgrade programs for multiple companies. DBMS DD See: Data Dictionary dependency In PMC, the relation between solutions. Dependencies are
defined at the PMC distributor side and are part of the meta data of a PMC
solution and guarantee that PMC solutions are installed in the correct
configuration and sequence at the PMC recipient side. The following values indicate the dependency type between solutions. Three dependency types are available: You can only install solutions that are dependent on other solutions if the other solutions are already present, or are also installed. The same dependency types exist between patches. However, to keep the descriptions readable, only solutions are mentioned, but patches are meant as well. One exception applies: the post-requisite type is not applicable to patches. derived product A product that is derived from a parent master product. The
parent product can, for example, be a main LN version such as LN 6.1. In general, the
derived product contains a subset of components from the parent product that
are changed and possibly a number of new software components. There are three categories of derived products: details session A dialog box that shows all the details (fields) of the line
(record) selected in the associated overview session. Use a details session to
view, enter, or change the data of one record. A details session can contain a number of tabs to group related fields. development VRC In PMC a physical VRC, derived from the Export VRC, in which checked-out software components are
temporarily stored during a change process. device A generic term for a computer subsystem. For example, a
printer, serial port, or a disk drive. DLL See: Dynamic Link Library domain A domain describes the properties of table fields. The main
property of a field is the data type, e.g. string, long, double, date, UTC.
Other properties are, for example, the length of a string, the alignment of a
string, and the date and time format. In the Chart Manager, a range with an initial value, an end value, and a step size. Domains indicate the valid values for an attribute and are used to define the scale division of the axes or to verify data. driver A hardware device or program that controls other devices. A
printer driver, for example, is designed to enable other programs to work with
a specific printer regardless of the printer's hardware specifications or
language. DUE See: Data Upgrade Engine dump To copy data to an external source. dynamic form A form with a dynamic form definition. The developer does not need to determine exactly where fields must be placed, or what they must look like. Instead, the developer defines:
At runtime, the dynamic form displays only those fields for which the user is authorized. Dynamic Link Library A means of sharing common functions between several programs.
This library contains functions for common use. The library can be linked to
the object as a function call at run time. Implementation of a dynamic link
library reduces the size of objects to a minimum because dynamic link libraries
are not included in a programs object. Acronym: DLL dynamic session A session with a dynamic form definition. Depending on specific settings, a dynamic session can start in these ways:
In the dynamic form definition, the developer does not need to determine exactly where fields must be placed, or what they must look like. Instead, the developer defines the form contents, the form structure, and the sequence of the objects on the form. At runtime the dynamic form displays only those fields for which the user is authorized. element A general term used for entities defined in LN, such as items,
business partners, currencies, and so on. The details of an element are
registered in the database as a record. In an overview session each element or
record is represented by a line. eMessage connector An interface between LN and various messaging providers, which is based on
XML and independent of the message protocol. For example, fax, telex, e-mail,
SITA, or SMS. encryption The process of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access,
especially during the transmission of data. You usually need a key to decode
encrypted data. expired If a software component, such as a session or a table, is set
to expired in a certain VRC, it cannot be used anymore in that VRC and in later
VRCs which were derived from the VRC where the component was set to expired. A software component that was set to expired is still available in preceding VRCs. export VRC The physical VRC from which components that belong to a PMC
solution must be exported at the PMC distributor side. Each base VRC has an export VRC linked, so components for
different products are exported from different physical VRCs. expression A combination of symbols that produces a result upon
evaluation. For example, identifiers, values, and operators. The resulting
value can then be assigned to a variable, passed as an argument, tested in a
control statement, or used in another expression. extension A derived product meant to fulfill requirements of a particular
line of business. Feature Pack See Service Pack. Acronym: FP field In table definitions, a field refers to a column. In a session,
a field is a specified area of a record used for a particular category of data. field help Help that explains the field's value and how it is used in the
session. Field help also mentions the default values and which values are
possible or allowed. Related topics point you to the related functionality in
the online manual. filter A means to selectively display specific information. In LN, two types of filters exist:
float A data type name used to declare variables that can store
floating-point numbers, that is, any number containing a decimal point, with a
maximum of 15 significant digits (8 bytes). font A set of characters of the same typeface, style, and weight.
For example Arial, in italic, and bold. form A screen that appears when a session is started. A form
interacts with the database, and provides the user interface that is used to
manipulate the data on the form. form command A command:
form field A field that is shown on a form. A form field is selected from
the available fields of an input table and its reference tables. FP See: Feature Pack function A piece of program code that makes up part of a program script. A function is a self-contained software routine that can perform a task for the program in which the function is written, or for another program. glossary Definitions of the terms used in LN. graph A graphical representation of information in a coordinate
system. Quantities are represented by bars, lines, symbols, or combinations of
these. graph series A number of data points that are linked graphically by means of
a line, a number of symbols, bars, or combinations of these. group A set of form objects grouped together. Examples of form
objects are form fields and child groups. group-by field A field on an overview form that is positioned above the grid.
The group-by field determines what is shown in the grid of an overview form.
Only the records that belong to the group-by fields are shown in the grid, for
example, all orders that belong to a specific customer. The name of the
customer is shown in the group-by field, the records are shown in the grid. help components Several sorts of online help used in LN. The help components in LN are:
help topic The code of the help text that is used to link help texts to
software components. Each text has a help text code and belongs to a package
VRC. index One or more table fields used to sort and search records in a table. A table must have at least one index. The first
index is always the Primary key. Infor Environment and Configuration Selector A tool that makes it possible to run different BW versions on a single client. Acronym: BECS installation run In PMC, a group of solutions that were installed together. This
can be a range of solutions, a solution with pre-requisites, or a combination of both. integrated session The session and the session's form are integrated into one
object. The form is a subcomponent of the session. When you perform an operation, for example, copy, delete, check-in, or checkout, on an integrated session, you also perform the operation on the integrated session's form. A non-integrated session's form is a separate object. job One or more sessions and/or shell scripts that LN executes without user
interaction. You can schedule jobs to run periodically or at a specified time. job calendar A calendar that consists of a number of dates/times, which are
used to indicate the dates/time a periodical job must be executed. label A code that is used instead of language-dependent text in
forms, reports, and menus. A label consists of a name and a content
description. The content of a label can differ by language, but the label name
remains the same for all languages. language number A conversion of the language code to a number between 0 and 61.
The language number eliminates problems caused by the use of uppercase and
lowercase language codes. The language code corresponds to the language number
by the following convention: Language code range Corresponding language number
range 0 to 9 0 to 9 a to z 10 to 35 A to Z 36 to 61. Example Language code b = Language number 11 Language code B = Language number 37 library A collection of files, computer programs, or subroutines. library authorizations The set of sessions that can be used to print, display,
maintain, and convert the authorizations of a group with the same role has for
specific Dynamic Link Libraries. license A means to validate the system configuration request of the
customer. Lightweight Directory Access Protocol In computer networking, the Lightweight Directory Access
Protocol, or LDAP, is a standardized networking protocol designed for querying
and modifying directory services. Acronym: LDAP LN 3GL A third-generation proprietary programming language that is a
mix of Basic and C. LN 4GL A fourth-generation language is a programming language designed
for interacting with the programmer used with relational databases. 4GLs are
event-driven. LN shell The LN shell is a program that runs the LN applications. The LN shell serves as an
interface program between the LN applications, operating system, user interface, and
database. This open systems architecture allows the LN applications to operate
on all supported combinations of operating systems, user interfaces, and
databases. Acronym: bshell Synonym: virtual machine LN software
environment The directory structure on the operating system that contains
the LN software and data
dictionary. Acronym: BSE LN user A person who uses the LN application. LN windows
interface A Windows-based interface program between the user and the LN servers. The LN windows interface runs
on the user workstation and communicates with the Bshell. Acronym: BW locale The character set and language used by a system. localization A derived product meant to fulfill country specific
requirements. log verb: To create a record of transactions or activities that
take place on a computer system. noun: A record of transactions or activities
that take place on a computer system. logical company Company as seen by the application. The sessions and program
scripts of LN use the
logical companies without having to know the physical company where the tables
are actually stored. In the most simple situation, a table in a logical company is linked to a physical company with the same company number as the logical company. In that case, the logical company and the physical company are the same company. If you use logical logical table linking, a table in a logical company is linked to a physical company with a different company number. logical printer A logical printer is a set of printer devices. In some
environments several printers may be located in close proximity to one another
( same room/floor). They can be grouped together as a logical printer. When
output is directed to a logical printer, the printer daemon will check the
paper type of each printer. It will automatically direct output to the first
printer that contains the required paper type. long A data type specified in LN as any whole number
from -2147483648 to 2147483647. merge A process which creates a target VRC from a source VRC. message A notification that informs you about something. More
specifically, a message attends you to an event, error, warning, and so on.
Messages usually appear in a message window or logged in a file. If displayed
in a window, a message requires a confirmation: Click OK. Messages are distinguished from Questions, which always require a choice
response. message server A server that stores and sends messages to clients module A part of a package consisting of a number of related software
components, such as sessions, tables, program scripts, reports, forms and
menus. For example, the General Ledger module in Financials. A module code consists of three characters. For example, the General Ledger has the code "gld". multi occurrence A session that lists the available elements or records of one
type, and some of their details (fields). You can use an overview session to
view, sort, add, change, copy, and remove records. When you add or change a record a details session usually starts. In some cases, you can add and change records directly using the overview session. Native Language Support Native Language Support. The system to convert character sets
between different computer systems. In LN it normally refers to
conversion between the character set of the operating system (for example
Windows NT or UNIX) and the bshell. The native language is the character set
which is used by the operating system on which LN is
running. Acronym: NLS Network Information Service The Network Information Service or NIS is Sun Microsystems'
"Yellow Pages" (YP) client-server directory service protocol for distributing
system configuration data such as user and host names between computers on a
computer network. NIS/YP is used for keeping a central directory of users,
hostnames and most other useful things in a computer network. For example, in a
common UNIX environment, the list of users (for authentication) is placed in
/etc/passwd. Using NIS adds another "global" user list which is used for
authenticating users on any host. Acronym: NIS NIS NLS object model A set of defined object types. The model defines which object
types support Document Authorization. object type Defines a business object, or business document, such as a
sales order or a contract, in the context of Document Authorization. An object type consists of one or more tables, and specifies this information:
obsolete solution Obsolete solutions are an administrative aid to manage the
synchronization of updates at the PMC recipient side when you install a Service Pack. An obsolete solution does not contain
software components. operator A symbol or other character indicating an operation that acts
on one or more elements. original VRC The VRC that contains the software components that have to be
modified. These software components will be changed in the Development VRC. overview session A session that lists the available elements or records of one
type, and some of their details (fields). You can use an overview session to
view, sort, add, change, copy, and remove records. When you add or change a record a details session usually starts. In some cases, you can add and change records directly using the overview session. package A set of related modules that implements a complete part of the
functionality, for example, Enterprise Planning, Financials, or Warehousing.
Packages are designed to function as independent as possible, to enable a
customer to implement only particular packages. A package code consists of two characters. For example, tt is the code of the Tools package. Each package has a unique version structure, the VRC structure. package combination A combination of several different packages with specific VRCs.
A package combination represents a complete usable version of LN. In the User Data (ttaad2500m000) session, each user is linked to a package combination, that determines which version of the software the user can use. In the Companies (ttaad1100m000) session, each company is linked to a package combination, to indicate which version of LN is appropriate to handle the data in that company. package VRC A version of a package, for example, tc B61O a cus1. In general, one version of a software component, such as a
session, a table, or a form, is stored in one particular package VRC. A developer can usually modify software components only in a particular package VRC. The code of a package VRC consists of:
package VRC PAM paper type A particular type of paper that must be used for a printer. The
paper type must correspond with the paper type in the printer. password A password is a form of secret authentication data that is used
to control access to a resource. The password is kept secret from those not
allowed access, and those wishing to gain access are tested on whether or not
they know the password and are granted or denied access
accordingly. password aging Password aging is a technique used by system administrators to
defend against bad passwords within an organization. Password aging means that
after a set amount of time, usually 90 days, the user will be prompted to come
up with a new password. The theory behind this is that if a user is forced to
change his password periodically, a cracked password is only useful to an
intruder for a limited amount of time. The downside to password aging, however,
is that users are more likely to write their passwords down. With password
aging the system administrator can set minimum and maximum lengths of time for
which the password is valid. Maximum time lengths force users to change
passwords regularly. Minimum lengths prevent users from quickly changing the
passwords back. patch In PMC, a patch is a collection of Solutions. In general a patch contains solutions created
in a larger time period. The patch entity is both known at the PMC distributor and PMC recipient side. Patches are an indivisible set of
solutions. You cannot install or uninstall individual solutions that belong to
a patch at the PMC recipient. You can only install or uninstall patches as a
whole. Yo can define dependencies between patches. Patches leave the Base VRC that is linked to the update VRC at the PMC recipient unchanged. The existing
PMC registry will remain and will be extended with data of the newly installed
patch. Patches only permit the most recent version of software components to be
maintained. Patches in general mainly contain corrective solutions. Note In PMC versions earlier than LN 6.1, the synonym Service Packs was often used for patches. periodical job A job that can be executed more than once. For a periodical
job, you must specify a time interval or calendar. If desired, the job can be
automatically reactivated. physical company The company where the data is actually stored. You can link
tables in Logical companies to the corresponding tables of a
physical company. pie segment Represents a percentage of the total pie chart. Pluggable Authentication Modules Pluggable authentication modules or PAM are a mechanism to
integrate multiple low-level authentication schemes into a high-level API,
which allows for programs that rely on authentication to be written
independently of the underlying authentication scheme. PAM were first developed
by Sun Microsystems, and are currently supported in AIX, HP-UX, Solaris, Linux,
FreeBSD and NetBSD. Acronym: PAM PMC PMC distributor The functional part of PMC that manages the creation of Updates. PMC Distributor is especially used by software
vendors who create updates. PMC recipient The functional part of PMC that manages the installation of Updates. Customers, who install updates in particular use
PMC recipient. PMC version The PMC version is linked to every Update and is intended to guarantee that various formats
of PMC solution dumps are handled by the right version of the PMC software.
Note Dumps created for a higher PMC version cannot be processed at the recipient side if PMC recipient has not been upgraded to that PMC version. Dumps of lower PMC versions can always be processed. porting set A collection of objects such as bshell, database, drivers,
printer daemon and so on, which can only run on the machines/operating systems
for which they are compiled/ported. post-requisite Post-requisites are mainly meant to prevent the installation of
bad solutions. In general, a post-requisite is a link from an earlier, bad
solution to a more recent, correct solution. pre-requisite Pre-requisites mainly steer the sequence in which solutions are
installed. In general a pre-requisite is the link from a more recent solution
to a predecessing solution. Pre-requisites are the most common type of
dependencies. A pre-requisite dependency exists between two solutions if one
solution must have been installed before the other solution is installed. In
that case, the first solution is a pre-requisite for the other solution.
Typically, pre-requisite dependencies exist between a solution and a previous
solution, if these solutions have one or more components in common.
Pre-requisite dependencies can only be created to solutions in the same Base VRC. primary key The unique identification for a record in a Table. printer daemon A networking program that permanently runs in the background
and handles the print requests issued by the users. When output is directed to
a logical printer, the printer daemon checks the paper type of each printer,
and then directs the output automatically to the first printer that contains
the required paper type. Product Maintenance and Control Product Maintenance and Control (PMC) is a tool that helps a
customer manage the updates of the LN system. With the PMC tool, you can check all patches against the customer's LN system to verify their completeness, check any potential interference with the customization, and detect dependencies. These capabilities ensure the complete and accurate installation of each software patch and Service Pack. In addition, using the PMC tool enhances the quality of the support being available to customers. PMC consists of a PMC distributor part and a PMC recipient part. Acronym: PMC program script A sequence of instructions that is used to program a number of
actions that must take place in addition to the standard program. Two different
program scripts are available, namely 3GL scripts and 4GL scripts. Synonym: UI script PVRC query The process of extracting information from a database and
presenting it in a report. question A notification that requires a choice response. For example, a
question can prompt you to confirm or cancel a delete action. If you do not
respond to a question, the process that prompted the question cannot continue.
Questions are distinguished from Messages, which
offer no choice and do not necessarily require a response. question mark button Changes the pointer into a question mark. To display pop-up
Help that briefly describes the command, click a menu command, a command
button, or a toolbar button with the question mark pointer. To display the field Help, click a field with the question mark pointer. RCS RDBMS record A data structure that is a collection of fields (elements),
each with its own name and type. The elements of a record represent different
types of information and are accessed by name. A record can be accessed as a
collective unit of elements, or the elements can be accessed individually. reference See: table reference reference mode The way in which a reference restricts the contents of a table
field. A reference can have one of the following reference modes:
reference table The table to which some table field refers. Example One of the fields of the Items – General table is the Country of Origin (coor) field. This field can contain a country code. (The field can also be left empty.) LN stores country codes in the Countries table. To control this connection, the table field Country of Origin in the Items – General table has a reference to the Countries table. Items – General is the referral table and Countries is the reference table. reference type The means by which a reference is defined.
referral table The table that has a field that refers to another
table. Example One of the fields of the Items – General table is the Country of Origin (coor) field. This field can contain a country code. (The field can also be left empty.) LN stores country codes in the Countries table. To control this connection, the table field Country of Origin in the Items – General table has a reference to the Countries table. Items – General is the referral table and Countries is the reference table. Relational Database Management System A relational database or database management system that
consists of tables made up of rows and columns. In a relational database, the
rows of a table represent records and the columns represent fields with the
particular attributes of a record. The records are collections of information
about separate items. The attributes of the records are represented in the
columns. The relational database management system uses data in a specified
column of one table to find additional data in another table. Acronym: RDBMS release An update in a version. For example, 'B61 a', where 'B61'
represents the version code, and the 'a' represents the release code. Each
update results in a new release with a new release code. replication See: data replication report A report is used to present data from the database, usually on
paper. The report can be sent to a device, such as a physical printer, a
display, or to a file. Revision Control System A tool, that is used by Tools to store revisions of scripts,
libraries, includes and report scripts. Acronym: RCS role From a user point of view, a function, or part of a function in
an organization. For example, manager, secretary, and so on. From an
authorization point of view, an identifying name for a group of users. A role
can contain several sub roles. SCM group A Software Configuration Management group in LN that identifies a
development group that has a separate development environment. Security Support Provider Interface Security Support Provider Interface (SSPI) allows an
application to use various security models available on a computer or network
without changing the interface to the security system. SSPI does not establish
logon credentials because that is generally a privileged operation handled by
the operating system. A security support provider (SSP) is contained in a
dynamic-link library (DLL) that implements SSPI by making one or more security
packages available to applications. Each security package provides mappings
between the SSPI function calls of an application and the functions of an
actual security model. Security packages support security protocols such as
Kerberos authentication and LAN Manager. Acronym: SSPI sequence file The file in which (a part of) the audit trail is
stored. server A program or system that performs a predefined task at request
of a user or another program or system. See also client. Service Pack In PMC, a Service Pack is a collection of solutions. In
general, a Service Pack contains solutions created in a larger time period. In
PMC the term 'patch' is also applied for Service Packs. The patch entity is
both known at the PMC distributor and PMC recipient side. A property in the
patch entity makes the difference between patches and Service Packs. Service
Packs are an indivisible set of solutions. You cannot install or uninstall
solutions that belong to a Service Pack at the PMC recipient. You can only
install or uninstall Service Packs as a whole. You can define dependencies
between Service Packs. Service Packs are intended to enable you to maintain
multiple Base VRCs in parallel. Service Packs change the base VRC
that is linked to the update VRC at the PMC recipient. The existing PMC
registry for the update VRC will be moved to history and a new registry will be
started for the update VRC. This type of patch in general contains a
significant amount of functional changes. Note Service Packs as described in the preceding definition do not exist in PMC versions earlier than LN 6.1. Acronym: SP service provider The software application that enables messaging, such as
Outlook or Fenestrae. session An elementary part of LN the user can start to
run an application's functionality. Usually, a session is linked to a main
database table and a program script. In addition, a session uses zero or more
forms, reports, and charts. The code of a session consists of a package code, a module code, four digits that indicate the main table number and the session type, an m or an s, and three additional digits, for example, Countries (tcmcs0510m000). session authorizations The set of sessions that can be used to print, display,
maintain and convert the authorizations that a group of users, that are
identified by a role, have for specific sessions. session group A group of sessions that are automatically started when a user
starts the bshell. session help Help that tells you how to use the session and what the result
will be. Notes and remarks draw your attention to any special information.
Related topics point you to a description of the related functionality in the
online manual. shared memory A part of physical memory intended for common use. Programs
communicate with each other through shared memory. The use of shared memory
results in faster access to the components loaded in shared memory. Before
starting the application, shared memory must be initialized and setup. A
prerequisite for using shared memory is that it should be supported by the
hardware besides having sufficient internal memory at its disposal. The following components can be loaded into shared memory:
shell command The program, at operating system level, which is executed
before the output is (re) written to a file. For example, this program can be a
conversion program to filter the input data. single occurrence A dialog box that shows all the details (fields) of the line
(record) selected in the associated overview session. Use a details session to
view, enter, or change the data of one record. A details session can contain a number of tabs to group related fields. Single sign-on Single sign-on (SSO) is a specialized form of software
authentication that enables a user to authenticate once and gain access to the
resources of multiple software systems. There are at least five major types of SSO or reduced sign-on systems in common use at the time of this writing (2005):
Acronym: SSO software component The LN software exists of the following separate software components: Software Configuration Management With software configuration management, a developer can modify
and test an own revision of a software component. Using a check-out and
check-in functionality, a software component is locked for others developers.
This method guarantees that no more than one developer can modify the same
software component at the same time. Acronym: SCM software language The language in which the software components, such as forms
and reports, are displayed. For each user, the default software language is
defined in the LN user
data. For more information, refer to Multilanguage application data. solution In PMC, the smallest, indivisible type of update. A solution is
identified both at the distributor and recipient side by a unique solution
code. The term individual solution is also frequently used and has the same
meaning. Note In the PMC software the term solution is often used as an alternative for the term update. A solution can then be an individual solution, which is the smallest, indivisible type of an update, or a patch. solution status distributor The following statuses describe the progress of the maintenance
of solutions, Collections, and patches. To keep the descriptions readable, only
solutions are described. However, in each case, collections and patches are
intended as well, unless explicitly excepted. The status of the solution is only used at the distributor side. A history of status changes is recorded in the Maintenance History table. To distinguish maintained solutions at the distributor side from imported solutions at the recipient side, the status is cleared when the solution is imported. This also applies to patches, but not to collections. The reason is that a collection is not known as such at the recipient side. Only the solutions contained in the collection are known at the recipient side.
solution status recipient The following statuses indicate the progress of the
installation or uninstallation of a solution or Patch. These statuses are only used at the recipient side, and must not be confused with the Solution status distributor at the distributor side.
SP See: Service Pack SSO See: Single sign-on SSPI standard program See: 4GL engine start-up menu The first menu displayed after LN is started. The start-up menu code consists of the:
status bar A line of information related to the application in the window.
Usually located at the bottom of a window. STP See: 4GL engine string A data structure that contains a number of characters that
represent readable text. strip 8th bit If you strip the 8th bit from a number, it means to remove the
8th digit in binary notation. Example 1111 1110 (binary) = FE (hexadecimal) = 254 (decimal) -> 111 1110 (binary) = 7E (hexadecimal) = 126 (decimal) When converting characters between different systems (for example, NLS to TSS), the 8th bit is stripped to obtain the intrinsic character value, which is sometimes needed to address the font. strip menu To set a number of menu choices that do not meet certain
conditions, to Inactive. substitution table A table that consists of two columns: a column with source
descriptions and a column with target descriptions. You use substitution tables
to do global search and replace actions in LN. The descriptions and
helptexts for the software components in LN are searched for the
substitution table's source descriptions. The source descriptions that are
found, are replaced by the target descriptions. superseded solution A superseded solution is a solution for which can be said that
all software components are also contained in another so-called Superseding solution. superseding solution A superseding solution is a solution that contains at least the
same software components as contained in one or more Superseded solutions and can contain additional software
components that are not part of any superseded solution. A solution supersedes another solution if the following conditions are met:
system administrator The person responsible for administering the use of a
multi-user computer system, communications system, or both. A system
administrator assigns user accounts and passwords, establishes security access
levels, and allocates storage space. table A data structure that is used to store data that consists of a
list of records, each entry being identified by a unique key and containing a
set of related values. A table contains a number of table fields that belong to
a specific domain. A table code consists of a package code, module code, and three digits. Example Table: tc mcs010 Countries
table linking A method of table sharing that stores a table physically in one
company (the physical company) and lets other companies (the logical company)
use that same table as if the table is their own. In the following diagram, company 200 shares some of the
tables of company 100. 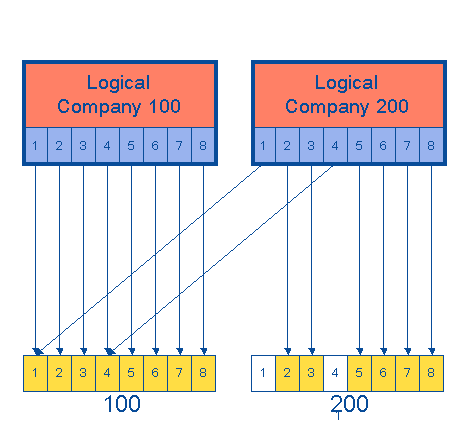 Table linking table reference A link to a table from which something must be selected or
where additional information about something is stored. Example The Items - General (tcibd001) table has a Country of Origin (tcibd001.ctyo) field . This field has a reference to the Countries (tcmcs010) table. If you enter a country code in this field, LN does the following:
Hard references are defined in the table definition. Soft references are not defined in the table definition, but programmed in a program script or dll. Synonym: reference table sharing A method to use the same data by more than one company. If a
user in one company creates, modifies, or deletes a record in a shared table,
the effect will be visible in all companies that share the table. Two techniques can be used to achieve table sharing:
template In the authorization management system (AMS), a method to
maintain common data for a group of users with the same role. text group A means to define how text must be presented in a window by
defining the text editor, default window, and dimensions of the window. textgroup authorization template A set of sessions used to print, display, and maintain
authorizations that a group of users share for a specific textgroup. The text group authorizations template is dumped to the user file of all users who use the specific template. transaction A logical unit of work, resulting in one or more changes on a
database that are carried out as an atomic entity. transaction notification A message that states that the data in the source database was
changed. Triton Super Set The collection of character sets used internally by LN. TSS character sets include ASCII (ISO 8859-1) characters and a range of multibyte character sets including sets of Japanese and Hebrew characters. Triton the name of a previous version of the LN software. Acronym: TSS TSS See: Triton Super Set tuple In the business object repository, a tuple is an instance of a
component. In the context of databases, a tuple is row in a table. The tuple
contains logically related data. The term originated as an abstraction of the
sequence: single, double, triple, quadruple, quintuple, ...
n-tuple. UI script See: program script undo check-out A command of Software Configuration Management that deletes the checked-out software component from the Development VRC. Universal Time Coordinated A time/date format. LN stores dates and times in UTC format. It stores both
date and time in a single Long integer referred to as the UTC long format. This
integer represents the number of seconds since 0:00 hour, January 1, 1970 (in
UTC). Acronym: UTC update In PMC, an update is a set of changed software components,
including PMC metadata, which is required to install the update in a safe and
correct way. An update can contain corrective changes or functional
enhancements. Updates can be delivered in four different configurations:
update VRC A physical VRC at the PMC recipient side in which updates are
installed. Every update VRC has a base VRC linked. upgrade program A DLL that contains the logic to upgrade a particular table
after installation of a more recent Feature Pack of LN. upgrade task The execution of an upgrade program for a particular company. user data template A template that contains system data and authorizations related
to a group of users. The data contained by the template is dumped to the user
file of all users who use the specific template. UTC version An upgrade of a package, for example, B61. Each change in the
functionality of a package results in a new version. A version can contain
several releases. Version - Release - Customer The version - release - customer (VRC) code is an
identification of a stage in the development of the LN software. An example of
a VRC is B61_a_ams. A VRC code consists of:
A VRC can be derived from a preceding VRC. Every software component that is contained in the preceding VRC and not explicitly modified or set to expired in the current VRC will also be available in the current VRC. Acronym: VRC Acronym: PVRC Synonym: package
VRC virtual machine See: LN shell VRC VRC combination A VRC Combination is defined at the PMC recipient side and
consists of a set of related Update VRCs. The VRC Combination will guarantee that, if
required, the related update VRCs are updated simultaneously at the PMC
recipient side. In this way, you can avoid compatibility problems between
related update VRCs. For example, if you use the standard application and you
also have an extension installed, you will have two update VRCs defined. If a
co-requisite dependency is defined between a standard solution and a solution
for the extension, PMC installs both solutions in one run if you linked the
update VRCs for both standard and extension in one VRC
combination. What's this? The pop-up Help that tells you briefly the functions of a tool
bar button, command button, or menu command. zoom session The session in which you can browse through the available
records and select a record. A zoom session is an overview session in read-only
mode. You can use a zoom session to enter the code of an existing record (for example, an item, order type, or warehouse) in another session. Click the browse arrow button behind the field or press CTRL+B to start a zoom session.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||