Offsetting from finish date to start dateOffsetting from the finish date to the start date, depends on the order type. Offsetting differs for production orders, purchase orders, and distribution orders. Offsetting production orders These factors determine how a production order is planned/offset:
Routing planning A production order includes a series of operations. The sequence of operations is managed by the routing. One item can have multiple routes, with various sets of operations, depending on order quantity. In addition, you can model phantom items, which result in a network of parallel operations. The impact of phantom items on planning is described later. One planned operation includes these lead time components:
Production time can be either quantity dependent or fixed, which is determined by the Fixed Duration check box. These options are available:
Production time = cycle time * order quantity / routing quantity
Production time = cycle time If you use the detailed routing information, the offsetting of two operations is as follows: 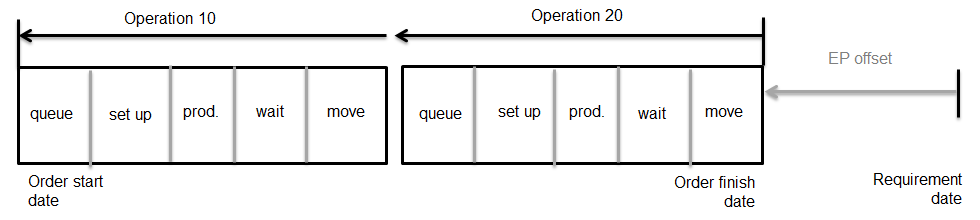 Production orders, offset operations Operation overlap The previous figure shows how you can plan two operations sequentially. Operation 20 starts when operation 10 is finished. If you use a transfer batch quantity or percentage, operation 20 can start when operation 10 is partly finished. 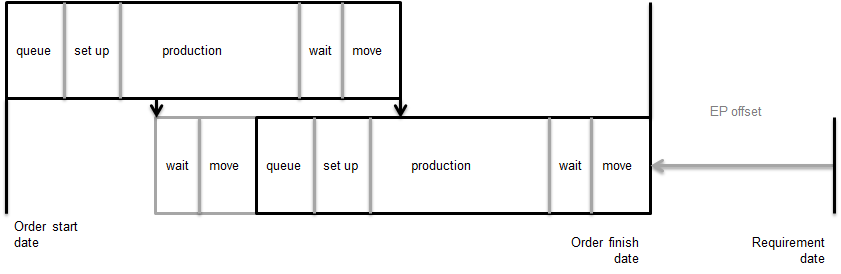 Production orders, operation overlap Network of phantom operations If item A has phantom items B and C as components, the production order contains the operations of item A, as well as of items B and C. If, for example, phantom B is required on the third operation of item A, and C is required on the second operation, the planning is as follows: 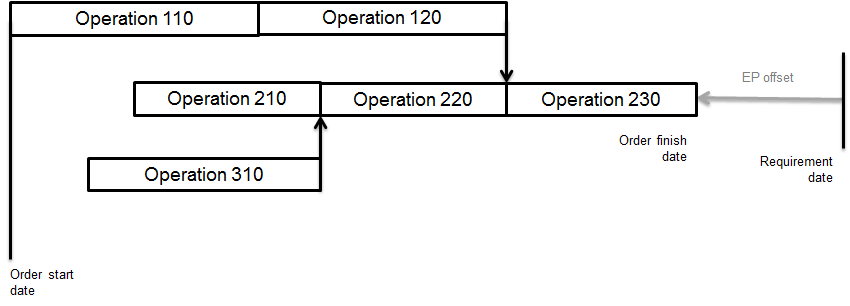 Production orders, network of operations Capacity The required capacity for a production order is derived from the operation lead times. Occupation factors indicate how many men or machines are involved in the operation. Only the setup time and the production time require capacity. For the two types of production times, the capacity calculations are as follows:
Man hours = average set up * man occupation for set up + cycle time * order quantity * man occupation for production / routing quantity Machine hours = average set up * machine occupation + cycle time * order quantity * machine occupation / routing quantity
Man hours = average set up * man occupation for set up + cycle time * man occupation for production / routing quantity Machine hours = average set up * machine occupation + cycle time * machine occupation / routing quantity In the Enterprise Planning resource plans, either man or machine capacity is stored based on the Critical Capacity for Planning field in the Work Centers (tirou0101m000) session.
| |||