Component CTP reservationsAssume the following multi-level bill of material for end item
JOSUEF11: 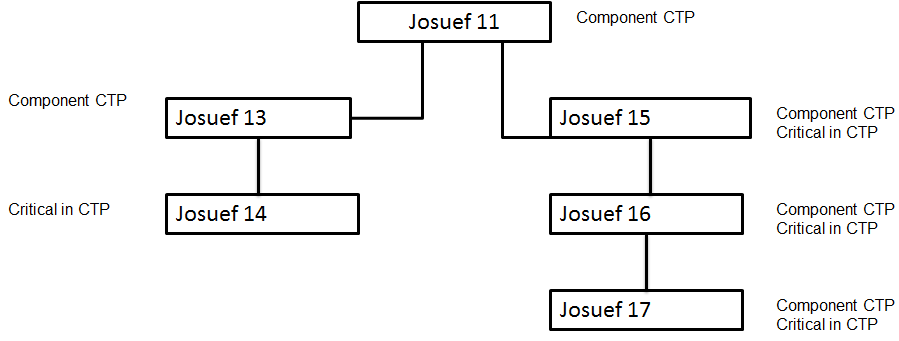 Component CTP reservations If you enter and save an order for JOSUEF11, CTP reservations are placed on the components based on the same logic as used for the CTP check. The CTP reservation is stored in the CTP reservations session, and aggregated to the item master plan in case the component has one. The timing of the component reservations is based on the lead-time offset logic that is also used during the CTP check. In other words, in the order horizon by means of the LTO on the BOM line, and the inbound and outbound lead-time, and the safety time and extra lead-time. The timing of the planned issue that is created after running the order planning can differ slightly from the CTP reservation, because timing of the planned issue is determined on a more detailed backward planning logic. The following quantities are used:
CTP quantity = Needed quantity - Allocated quantity Example Sales order demand for JOSUEF11 = 100 pieces. The following CTP reservations are created for the right-side branch of the BOM. The ATP column states the ATP quantities that are available during the CTP check. When you save the sales order line, the other columns are updated in the CTP reservations session.
The calculation proceeds:
Note Even if for the JOSUEF15 and JOSUEF16 items the Critical in CTP check box is cleared in the Items - Planning (cprpd1100m000) session, records are created in the CTP reservations sessions. This step is required to pass the needed quantity and CTP quantity through the BOM. However, the allocated quantity will always be zero for noncritical items, even if ATP is present for this type of item. Pegged order number field and originating plan item
field In the previous example, the CTP reservation of the component JOSUEF17 is made for the sales order for end item JOSUEF11. The originating plan item is the direct parent, JOSUEF16, because the quantities that you see in the figure are passed by means of this item. Capacity CTP reservations Capacity CTP depends on the presence of a resource master plan. Therefore, capacity CTP is plan-period based. The CTP reservation is stored in both the resource master plan and the capacity CTP reservations session. CTP reservations are created only for resources that are critical in CTP and have a resource master plan. CTP time fence A CTP time fence for component and capacity CTP can be defined in the Items - Planning (cprpd1100m000) session. In the CTP time fence, the availability of components and capacities will not be checked. This concept is introduced to prevent situations in which deliveries to customers are promised although this is not realistic because no time is available anymore to build extra quantities. In fact, the CTP time fence usually equals the item’s production time fence (frozen period for planning). The production time fence, also defined in the Items - Planning (cprpd1100m000) session, is used during order planning. The planned production order will be placed outside this time fence, although the demand may originate from within the time fence. This will create lateness. To assure that demand is not promised too early, only ATP can be promised inside the CTP time fence and not CTP. To give the user flexibility and to make it more explicit, a separate CTP time fence is available instead of using the production time fence.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||