Configuring an ActionEventMessage push webhook
This section explains how to configure an HTTP-based push function, or webhook, to enable event-driven communication between Landmark and an external server.
This diagram shows two methods for sending data to the Landmark server: push and pull.
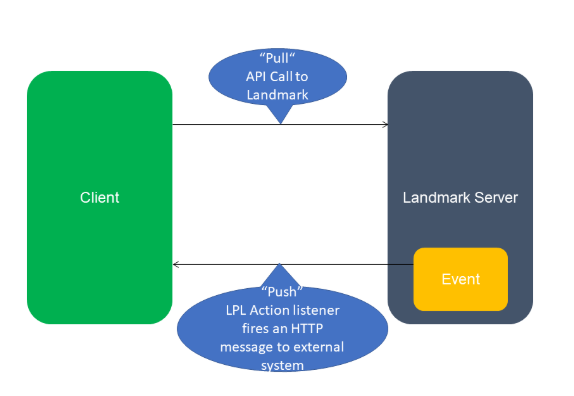
Pull API calls are used to check the state of a specific data instance. For example, a customer might issue an API call to Landmark as an incoming request to check a state. If the data is not in the required state for the action, the customer's API call would need to continually issue web service calls until the state is met (polling). In this client-server scenario, the customer's API call acts as the client, and Landmark serves as the server. This scenario is represented by the top arrow in the diagram.
Push calls allow customers to subscribe to specific business class action events through the ActionEventMessage business class. When an event (LPL Action) occurs, an HTTP-based, customer-configured message is sent to the endpoint. When the state of the instance is changed by the business class action, an outgoing message is pushed from Landmark to an external system. In this client-server scenario, Landmark acts as the client, and the server is the external target endpoint configured by the customer. This scenario is represented by the bottom arrow in the illustration.
The rest of this section outlines the steps for configuring an ActionEventMessage push webhook.
Perform all configurations in the data area from which the calls are run.
Before performing the steps in this section, ensure you have created a UserTemplate in JSON, XML, or text format that contains the outgoing message to be sent when the specified scenario in the call is encountered.