Working with the BPMN elements
To place an element on the canvas, click the element icon and then move the mouse to the location where you want to place it. Type a name and click outside of the element shape to confirm.
You can find other element types by using the wrench icon from the element context menu. The context menu is shown when an element is selected on the canvas.
After an element is placed on the canvas, you can edit its attributes in the panel on the right side:
- Main attributes to describe the general properties of this element type.
- Business attributes that contain industry-specific values.
- Cost and Resource Analysis attributes.
- Related documents to allow attaching documents specific to this element. For details, see Infor Document Management related documents.
To edit the attribute values, there are specific value pickers depending on the attribute type. In presentation mode, the attribute values for various elements are shown on the attributes panel that you can open and close when you click the element.
These attributes have a special meaning:
- The text or rich text type attributes can be edited in the BPMN Modeler, or they can be associated with a registry entry that has been predefined for reuse. For details, see Content translation.
- The Application Navigation attribute is used to define navigation links to other applications. For details, see Application Navigation.
- The Image attribute for the IT System element is used to select an image from the registry and place it on the canvas. In the registry, the administrator can upload SVG and PNG images into Image Library type categories. For details, see the Infor Process Intelligence Administrator Guide.
- The Subprocess Reference attribute in a Collapsed Subprocess element is used to navigate to the BPMN diagram that describes this collapsed subprocess. In presentation mode, double-click the collapsed subprocess element to navigate to the referenced diagram.
- The Diagram Links attribute used in Intermediate Catch and Throw events helps you navigate preceding or following diagrams for these events. If there is only one diagram link defined, you can navigate in presentation mode by clicking the element on the canvas. If several diagram links are defined, these are displayed in presentation mode as clickable links in the attributes panel.
Basic elements in the palette
This table gives an overview of the BPMN elements available on the palette:
| Element | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
| IT-System |  |
An IT system refers to a hardware device used to perform tasks, such as a barcode scanner, or a software application executed on another system, such as initiating a workflow or using e-signature. You can change the icon in the Element attributes panel. |
| Message |  |
Indicates a message flow. |
| Start Event |  |
Indicates the beginning of a process. There are several types of start events, which you can select from the context menu. |
| Intermediate/Boundary Event |  |
Intermediate events occur between the start and end of a process. They indicate points where specific action takes place during the process, for example a timed event, an error or an exception.
There are several types of intermediate events, which you can select from the context menu. |
| End Event |  |
Indicates the completion of a process.
There are several types of end events, which you can select from the context menu. |
| Gateway |  |
Controls the flow of a business process by defining decision points. A gateway ensures that the correct sequence of tasks is followed depending on the process conditions.
There are several types of gateways, which you can select from the context menu. |
| Task |  |
Tasks or activities represent a unit of work that needs to be performed as part of the process. Tasks can be atomic (indivisible) or expanded into sub-processes.
There are several task types, which you can select from the context menu. |
| Sub-Process |  |
Represents a sub-process within the main process. Use Sub-Processes to break down complex processes into smaller, more manageable parts. |
| Data Object Reference |  |
Represents data or information used or produced within a process. It helps illustrate the flow of data between activities. |
| Data Store Reference |  |
Represents a place where data is stored during the process. It can be a physical repository or a database. |
| Pool/Participant |  |
Pools and Lanes are visual elements used to divide a process into specific sections, each related to a participant, role, department, or system involved in the process. This helps in identifying the responsibilities and interactions among different stakeholders. |
| Group |  |
Visual elements that help label or annotate areas in a business process, highlighting parts of the process without creating a sub-process. |
All supported element types
This tables gives an overview of all supported element types that are interchangeable from the context menu:
| Type | Supported Elements | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | Task |  |
Represents a task or operation performed in the process.
There are several task types with a specific meaning, which you can select from the context menu. |
| Call Activity |  |
Represents a call to a global process or a reusable sub-process defined outside of the current process. Use it to modularize processes and reuse them in different contexts. | |
| Sub-Process |  |
Represents a sub-process within the main process. Use Sub-Processes to break down complex processes into smaller, more manageable parts. | |
| Event | Start Event |  |
Indicates the beginning of a process. When a simple start event is used, the process starts immediately without an external trigger. There are several types of start events, which you can select from the context menu. |
| Intermediate/Boundary Event |  |
Occurs between the start and end of a process. It indicates a point where specific action takes place during the process, for example a timed event, an error or an exception.
There are several types of intermediate events, which you can select from the context menu. |
|
| End Event |  |
Indicates the completion of a process.
There are several types of end events, which you can select from the context menu. |
|
| IT-System/ Message | Message |  |
Indicates a message flow. |
| Traffic Light |  |
A variation of the Message element used to model operational insights. | |
| Indicator |  |
A variation of the Message element used to model operational insights. | |
| Cockpit |  |
A variation of the Message element used to model operational insights. | |
| IT System |  |
An IT system refers to a hardware device used to perform tasks, such as a barcode scanner, or a software application executed on another system, such as initiating a workflow or using e-signature. You can change the icon in the Element attributes panel. | |
| Start Event | Message Start Event |  |
Indicates that the process starts when a message is received. |
| Timer Start Event |  |
Indicates that the process starts based on a predefined time or timer. | |
| Conditional Start Event |  |
Indicates that the process starts when a specified condition is met. | |
| Signal Start Event |  |
Indicates that the process starts when a signal is received. | |
| Start Multiple Event |  |
Indicates that any one of the multiple events can start the process. | |
| Intermediate/ Boundary Event | Message Intermediate Catch Event |  |
Represents the receipt of a message during the process. |
| Message Intermediate Throw Event |  |
Represents the sending of a message during the process. | |
|
Timer Intermediate Catch Event |
 |
Represents an intermediate point in the process based on a timer or specific time. | |
|
Escalation Intermediate Throw Event |
 |
Represents the occurrence of an issue or event during the process. | |
|
Conditional Intermediate Catch Event |
 |
Represents an intermediate point based on a specified condition. | |
|
Link Intermediate Catch Event |
 |
Represents the use of a link to connect different parts of the process. It works with the Diagram Links attribute to navigate to preceding business processes. | |
|
Link Intermediate Throw Event |
 |
Represents the use of a link to connect different parts of the process. It works with the Diagram Links attribute to navigate to subsequent business processes. | |
|
Compensation Intermediate Throw Event |
 |
Represents the initiation of compensation activities in case of an error or exception. | |
|
Signal Intermediate Catch Event |
 |
Represents the receipt of a signal during the process. | |
|
Signal Intermediate Throw Event |
 |
Represents sending a signal during the process. | |
| End Event | Message End Event |  |
The process is concluded with sending a message. |
| Escalation End Event |  |
Represents a point in the process where an escalation happens due to a specific condition or situation necessitating intervention. This event triggers an escalation signal, alerting other processes or higher authority to address the issue. | |
| Error End Event |  |
Represents a specific point in a business process where the process is terminated due to an error condition. | |
| Compensation End Event |  |
Indicates the conclusion of a process that triggers compensation. It involves activities that undo or mitigate the effects of previously completed tasks, in case of a cancellation or rollback. | |
| Signal End Event |  |
Represents a specific point in a process where the process is concluded with sending a signal. This event is useful for broadcasting a message to other processes or components within the system, indicating that a particular activity is completed. | |
| Terminate End Event |  |
Signifies the immediate termination of an entire process. Upon encountering this event, all activities within the process are halted, and no further actions are carried out. |
|
| Gateway | Parallel Gateway |  |
Represents a point where multiple paths can be taken in parallel, without evaluating conditions. Used to start activities that run simultaneously. |
| Inclusive Gateway |  |
Represents a decision point where multiple paths can be taken based on evaluating conditions associated with each outgoing sequence flow. All paths with true condition are taken. | |
| Exclusive Gateway |  |
Represents a decision point where only one of the outgoing paths can be taken. The decision is based on evaluating conditions associated with each outgoing sequence flow. | |
| Complex Gateway |  |
Represents a more complex decision point where conditions and rules may involve a combination of logical operators. It allows for more sophisticated decision-making logic. | |
| Event-based Gateway |  |
Represents a decision point based on events. It is used when the process flow depends on the occurrence of specific events, such as receiving a message or a timer event. | |
| Task | Send Task |  |
Represents a task that sends a message or signal to another process or participant. |
| Receive Task |  |
Represents a task that waits for a message or signal to be received before proceeding. | |
| User Task |  |
Represents a task that requires human interaction. It is typically performed by a knowledge worker or end-user. | |
| Manual Task |  |
Represents a task that is performed manually by a human but it is less specific than a User Task. | |
| Business Rule Task |  |
Represents a task that is based on business rules or decision logic. It is often used for decision-making within the process. | |
| Service Task |  |
Represents an automated task that is performed by a software service or system. It may involve communication with external systems. | |
| Script Task |  |
Represents a task that is performed based on a predefined script or script language. It is typically automated. | |
| Sub Process | Collapsed Sub Process |  |
Represents a sub-process where details are not visible within the parent process diagram. It is used to simplify the main process diagram by encapsulating complex activities, while presenting a high-level overview. |
| Transaction |  |
Represents a specialized type of a sub-process. It makes sure that all enclosed activities are completed successfully or rolled back in case of an error. | |
| Event Sub Process |  |
Represents a specialized type of a sub-process that is triggered by an event. These events can be of various types, such as message events, timer events, or error events. Event Sub-Processes ensure that the process can adapt and respond appropriately to unforeseen events, enhancing the overall robustness and flexibility of the process model. | |
| Expanded Sub Process | 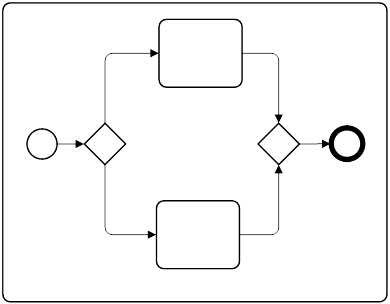 |
Represents a detailed sub-process where contents are fully visible within the parent process diagram. | |
| Data Object | Data Object |  |
Represents data or information used or produced within a process. It helps illustrate the flow of data between activities. |
| Data Object Collection |  |
Represents a group of related data objects used or produced within a process. | |
| Data Store |  |
Represents a place where data is stored during the process. It can be a physical repository or a database. | |
| Pool/ Participant | Expanded Pool/ Participant |  |
Represents separate organizational entity or participant in a process. Each pool can contain its own set of activities and processes, and communication between pools is depicted using message flows. |
| Lane |  |
Subdivision within a pool used to organize and categorize activities further. Each lane typically corresponds to a specific role, department, or system within the organizational entity represented by the pool. | |
| Empty Pool/Participant |  |
Represents a related process which does not need to be described in detail at the same time as the current process model. It is used to model the messages to be exchanged between the current process and the process represented by the collapsed pool. | |
| Flow | Sequence Flow |  |
Represents the order in which activities or events are performed within a process. It connects two flow objects, indicating the direction of the process flow. |
| Message Flow |  |
Represents the flow of messages between participants or pools in a process. It illustrates the communication paths between different entities. | |
| Association |  |
Connects artifacts, data objects, or text annotations to flow objects, indicating a relationship or dependency. Associations help in clarifying connections between elements. | |
| Artifact | Group |  |
Groups related elements in a diagram. It is used to visually organize and highlight specific sections of the process. |
| Text Annotation |  |
Provides additional information or comments to enhance the understanding of the process. Annotations are often used to add explanatory notes or documentation. |
Activity Markers
You can enhance activities such as Tasks, Sub-Processes, and Call Activities by applying markers that indicate specific behavior or characteristics. To add a marker, use the top bar of the context menu.
This table gives an overview of the supported markers:
| Marker | Icon | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ad hoc |  |
Indicates that the tasks within the sub-process can be performed in any order or repeated as needed. |
| Loop | 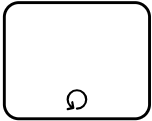 |
Indicates that the associated activity or sub-process are repeated in a loop until a certain condition is met. |
| Parallel |  |
Indicates that the tasks within a sub-process can be performed in parallel. |
| Sequential |  |
Indicates that the tasks within a sub-process are performed sequentially. |