Replication Rules form
You set up the replication rules in the Replication Rules form at each site. The spreadsheet you create in this step is the basis for the rules you set up. You can copy and paste rows from the spreadsheet into the grid view of this form.
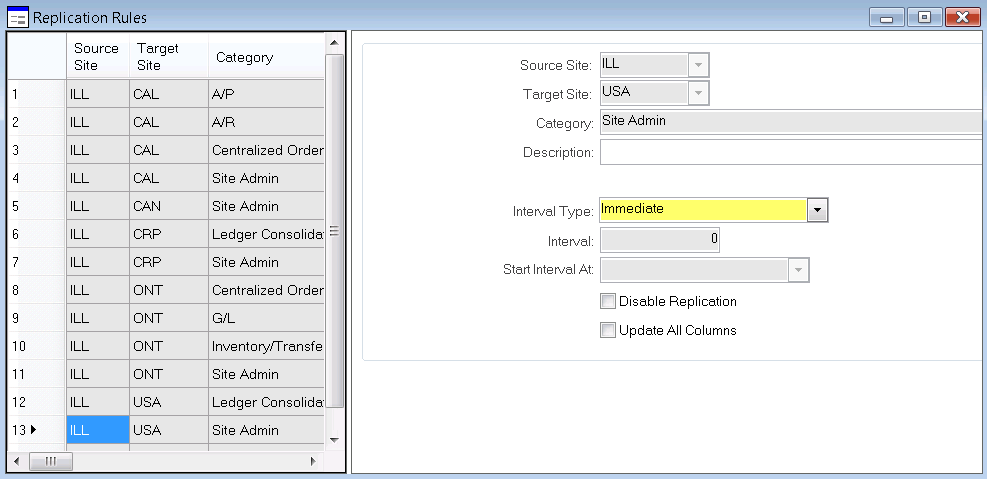
Interval Type, Interval, and Start Interval At field usage
For each rule, use these three fields together to specify the interval at which replication will occur. For example, you might choose an interval type of Minutes and then specify 90 in the Interval field. All interval types except transactional are non-transactional, which means that there is no live connection to another site.
These interval types are available:
- Transactional: Provides a live constant connection from one site to another. Updates are made to the remote site immediately. No interval or start time is required.
- Immediate: Immediately sends the replicated data to the replication queue. This setting does not mean that the data is shown immediately in the other site. It depends on how soon the queue is retrieved by the other site. No interval or start time is required.
- Minutes: Replicates data every nn minutes, where nn is the value specified in the Start Interval field.
- Hours: Replicates data every nn hours, where nn is the value specified in the Start Interval field.
- Days: Replicates data every nn hours, where nn is the value specified in the Start Interval field.
Update All Columns field usage
Specify Update All Columns for a rule if you want every table column included in that category or rule to be updated on the target site even if it wasn't changed by a user interaction on the local site. This is not recommended for replication, due to the high data traffic it may generate.
If Update All Columns is not specified, replication occurs only for the columns that have been changed.
Rule execution
Replication happens chronologically, based on the order things happened in the source system. For example, an order line cannot be added until after the order is added. So, when looking at the list of tables in a category, the replication process changes data from the listed tables in the proper order - it does not simply run down the list of tables alphabetically to determine what is different.