Intranets
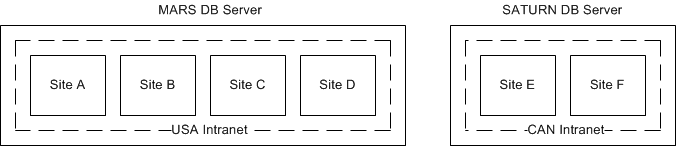
Usually, all the sites on the same LAN and/or database server will belong to the same intranet, and usually sites on different database servers are in different intranets, as shown in this flow chart:
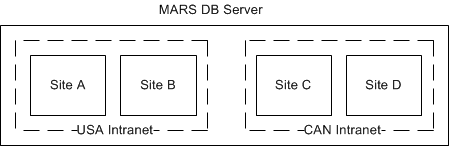
However, it is possible to set up sites on the same database server that are in different intranets, as shown in this flow chart:
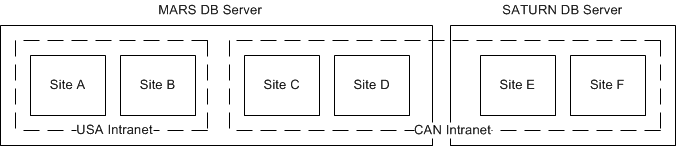
It is also possible to set up one intranet with sites on different servers, as shown in this flow chart:
If you have multiple sites in a single application database, and if the sites are sharing _all or user tables (through the Intranet Shared Tables or Intranet Shared User Tables utilities), then all sites in that database must be on the same intranet.
Generally, transactional replication should be performed only between sites on the same database server, for performance reasons. However, if your database servers are on a very fast network, transactional replication between sites on different servers is possible.
When a system includes multiple intranets on different servers, the data generally should be transferred between intranets through non-transactional replication (XML documents). When the schema in the source and target databases are not identical—for example, SyteLine to another application that uses Mongoose, or different versions of your application—an XSL transformation (style sheet) should be used. Each intranet has an ASP page that provides intranet access to the inbound queue. The ASP is the gateway to other databases. The address of the ASP is defined on the Intranets form.