Math Functions and Operators
Derive new calculations through the combination of multiple base measures and the use of a broad range of math operators.
Math Operators
As an example, to define a Revenue measure based on the two existing measures Sum: Quantity and Avg: Unit Price enter this expression:
[Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*[Order_Date: Avg: Unit Price]
BQL supports standard operators including:
- = equals
- * times
- + plus
- / divided by
- - minus
- % modulo
- < less than
- > greater than
- <> not equal to
- <= less than or equal to
- >= greater than or equal to
- AND
- OR
- LIKE
- NOT LIKE
- IS NULL
- IS NOT NULL
Math Functions
BQL provides functions for advanced mathematics.
- Absolute Value: ABS
- ABS provides the absolute value of a measure value.
-
Syntax:
ABS([measure]) -
Example:
SELECT ABS([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]) FROM [ALL]
- Arccosine: ARCCOS
-
The ARCCOS function returns the arccosine of a value between ο and π.
ARCCOS([logical_column])
-
- Arcsine: ARCSIN
-
Returns the arcsine of a number between -π/2 and π/2.
ARCSIN([logical_column])
-
- Arctangent: ARCTAN
-
Returns the arctangent of a number between -π/2 and π/2.
ARCTAN([logical_column])
-
- Arctangent of two: ATAN2
-
Returns the arctangent of x and y.
ATAN2(x,y)
-
- Rounding Up: CEILING
-
CEILING rounds up to the closest integer greater than or equal to the given number.
CEILING([measure])
-
- Cosine: COS
-
Returns the cosine of a given angle.
COS([logical_column])
-
- Radians to degrees: DEGREES
-
Converts x radians to degrees.
DEGREES(x)
-
- Exponent: EXP
-
Returns e raised to the power of the number given.
EXP([logical_column])EXP([OrderDate: Sum: Quantity])
-
- Rounding Down: FLOOR
-
FLOOR rounds down to the closest integer less than or equal to a given number.
FLOOR([logical_column])FLOOR([OrderDate: Sum: Quantity])
-
- Natural Logarithm: LN
-
Returns the natural logarithm of a given number in a specified base..
LOG([measure | numeric_attribute])
-
- Log Base e: LOG
-
Log base e of x
Returns the logarithm of a given number in a specified base.
LOG([measure | numeric_attribute])
-
- Log Base 10: LOG10
-
Log base 10 of x
LOG10([measure | numeric_attribute])
-
- Middle Value: MEDIAN
-
MEDIAN returns the value in the middle of all measure values at the report grain. It supports an optional BY break by attribute.Note: MEDIAN is not supported for use in the input statement of a scripted data source (ETL).
MEDIAN supports breaking attributes that instruct the query engine to re-calculate the median based on values changing for a particular attribute.
MEDIAN([measure] BY [attribute])For example:
SELECT [Products.Categories], MEDIAN([Order_Date: Sum: Revenue] BY [Products.Categories]) FROM [ALL]Categories MEDIAN([Order_Date: Sum: Revenue], BY) Desktops 150,413,715 Mobile Phones 101,721,700 MP3 Players 27,047,423 Notebooks 180,664,684 Tablets 204,825,336
-
- PI
-
Returns Pi (3.14159265…).
PI()
-
- Power: POW
-
POW raises the power of the first argument (x) to the power of the second argument (y).
POW(x,y)POW([measure | numeric_attribute],[measure | numeric_attribute])
-
- Running Sum: RSUM
-
Use RSUM to traverse the current result set to do running sum window based calculations. For example, the following RSUM formula requires a window size and calculates the trailing sum of values at the current report grain for the window provided.
RSUM(window_size_integer, [measure])For example, using Northwind data, show the running sum for different values of last N, showing that N is the same as the measure itself.
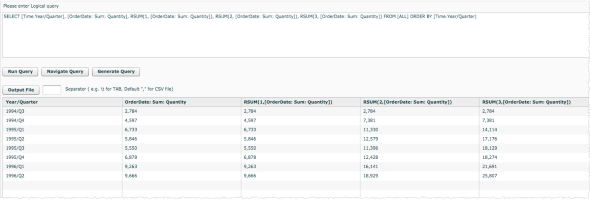
-
- Signum: SIGN
-
The SIGN function returns +1 for x > 0, 0 for x == 0, and -1 for x < 0.
SIGN([measure | numeric_attribute])
-
- Sine: SIN
-
The SIN function returns the sine of a given angle.
SIN([measure | numeric_attribute])
-
- Square Root: SQRT
-
The SQRT function returns the square root of a measure.
SQRT([measure])
-
- Tangent: TAN
-
The TAN function returns the tangent of a given angle.
TAN([measure | numeric_attribute])
-