Report authors can create pre-aggregate expressions, also called "push-down expressions", in Visualizer and Designer. Pre-aggregate expressions are evaluated in the Birst database. Evaluating expressions at the database level improves performance, and provides support for complex expression logic to create custom attributes and custom measures.
Important: Before using this feature
Pre-aggregated expressions apply at the space level and are enabled by default from the Push Down Expressions to Database space setting. You can disable it in Admin> Manage Space> Space Properties:

Important:
- If enabled, expect the results of existing report expressions to change because the expression is now aggregated in the database.
- The Push Down Expressions to Database feature supports all report expressions except those that include positional calculations and dimensional expressions. To use these, you must disable Push Down Expressions to Database.
- If you are using Smart Insights, you must disable Push Down Expressions to Database for new spaces.
Once enabled, you can create custom attributes and measures in the Visualizer Expression Builder or the Designer Expressions dialog.
Custom attributes and measures are based on BQL expressions syntax.
Aggregation Rule Operators
For custom measures, aggregation rule operators perform the equivalent of specifying aggregation rules.
The entire BQL expression is enclosed using an aggregate rule operator.
For example, a SUM aggregation:
SUM([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*2)
For another example, an AVG aggregation:
AVG([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*2)
If an aggregate operator is not specified, SUM is taken as the default aggregation.
Examples of Pre-Aggregate Report Expressions
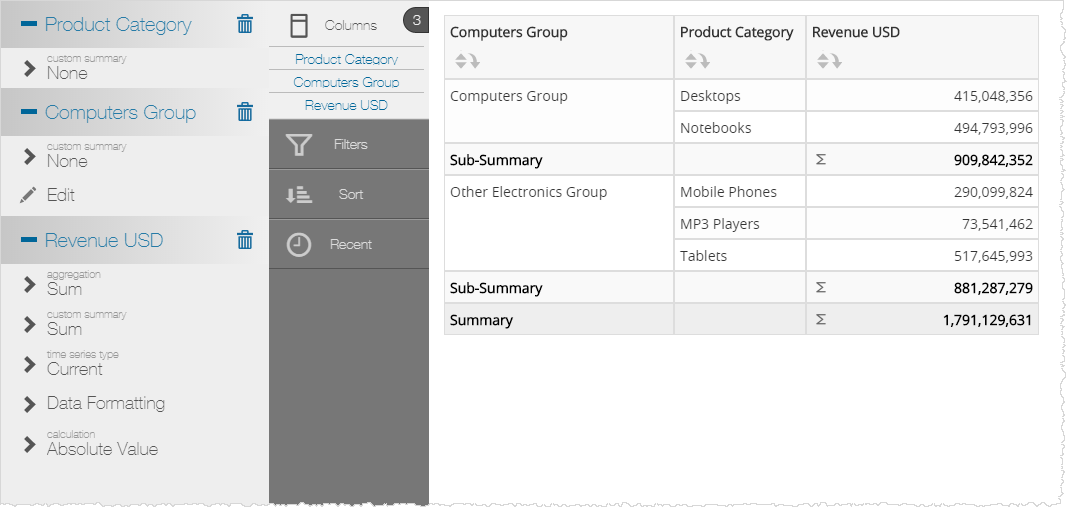
Custom Attribute / Custom Group Example
Example Expression
IIF([Products.Product Category] IN ('Desktops','Notebooks'),'Computers Group','Other Electronics Group')
Logical Query
SELECT USING OUTER JOIN IIF([Products.Product Category] IN ('Desktops','Notebooks'),'Computers Group','Other Electronics Group') 'COL0' , [Order_Date: Sum: Revenue USD] 'COL1' FROM [ALL]
Expression in Visualizer

Results in a Visualizer Report
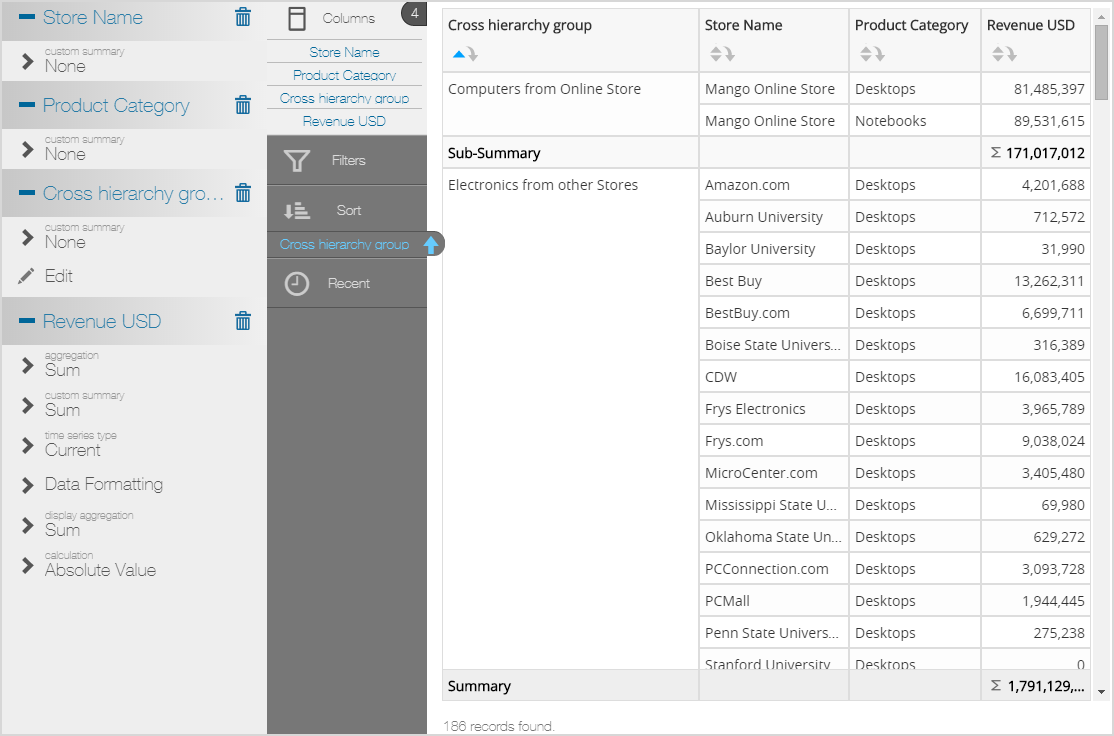
Cross-Hierarchy Custom Group Example
Expression
IIF([Products.Product Category] IN ('Desktops','Notebooks') AND [Stores.Store Name] = 'Mango Online Store', 'Computers from Online Store','Electronics from other Stores')
Logical Query
SELECT USING OUTER JOIN IIF([Products.Product Category] IN ('Desktops','Notebooks') AND [Stores.Store Name] = 'Mango Online Store', 'Computers from Online Store','Electronics from other Stores') 'COL0' , [Order_Date: Sum: Revenue USD] 'COL1' FROM [ALL]
Expression in Visualizer

Results in a Visualizer Report
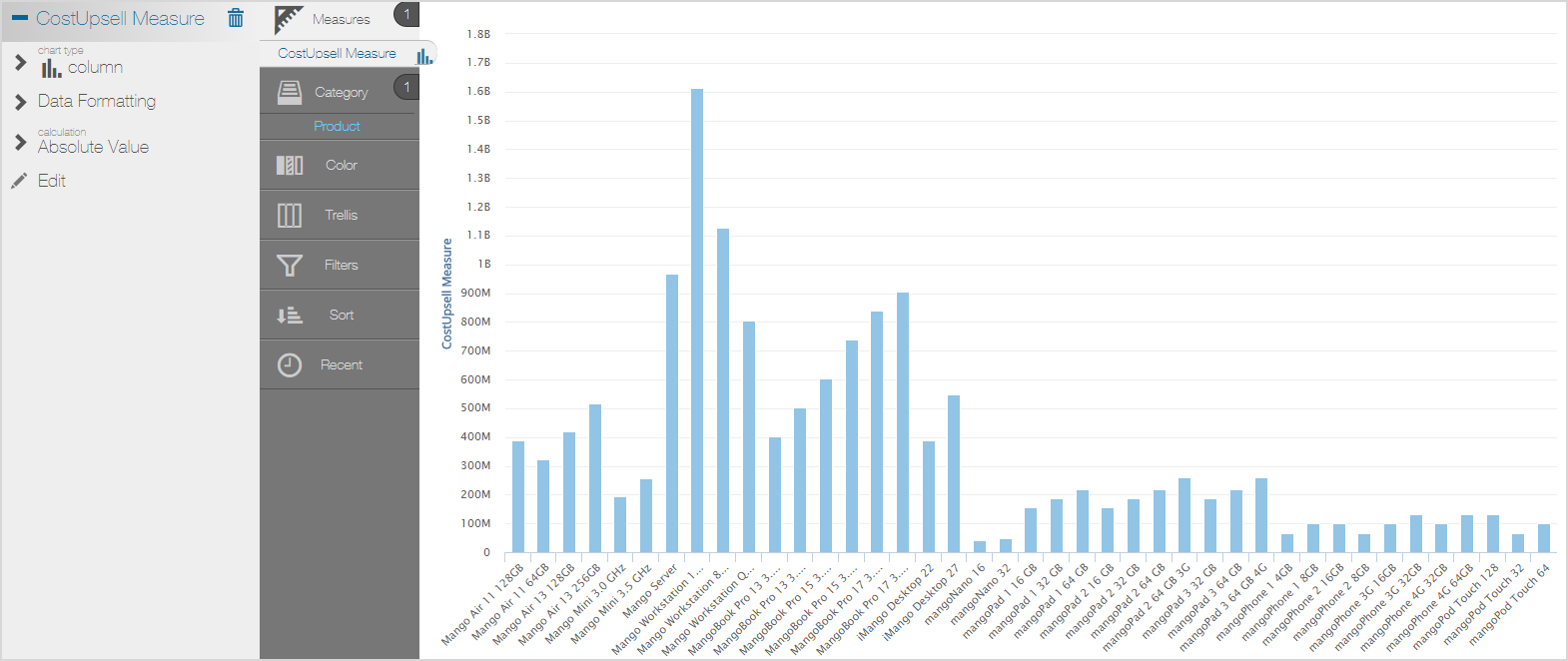
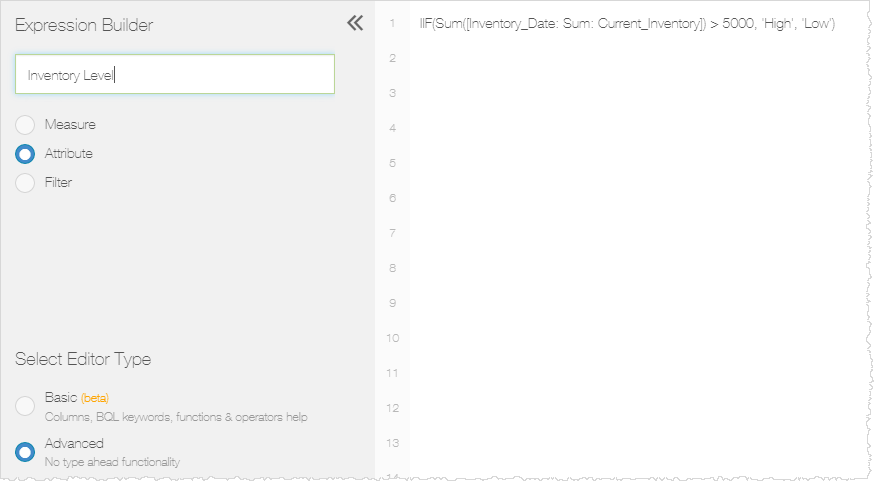
Custom Attribute Based on a Measure Example
Expression
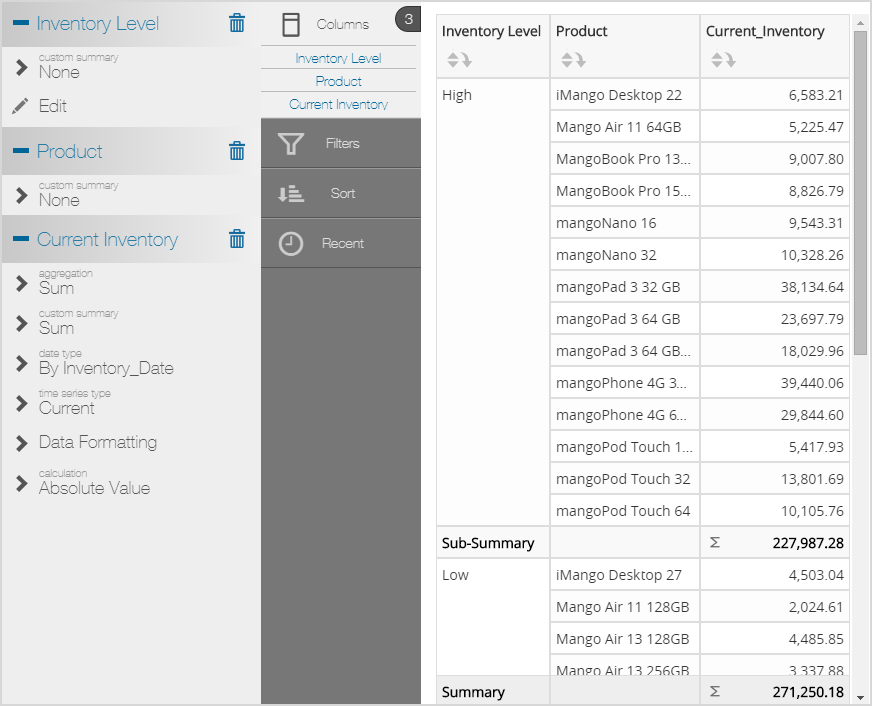
IIF(Sum([Inventory_Date: Sum: Current_Inventory]) > 5000, 'More', 'Less')
Logical Query
SELECT USING OUTER JOIN IIF(Sum([Inventory_Date: Sum: Current_Inventory]) > 5000, 'High', 'Low') 'COL0' , [Inventory_Date: Sum: Current_Inventory] 'COL1' , [Products.Product] 'COL2' FROM [ALL]
Expression in Visualizer
Results in a Visualizer Report
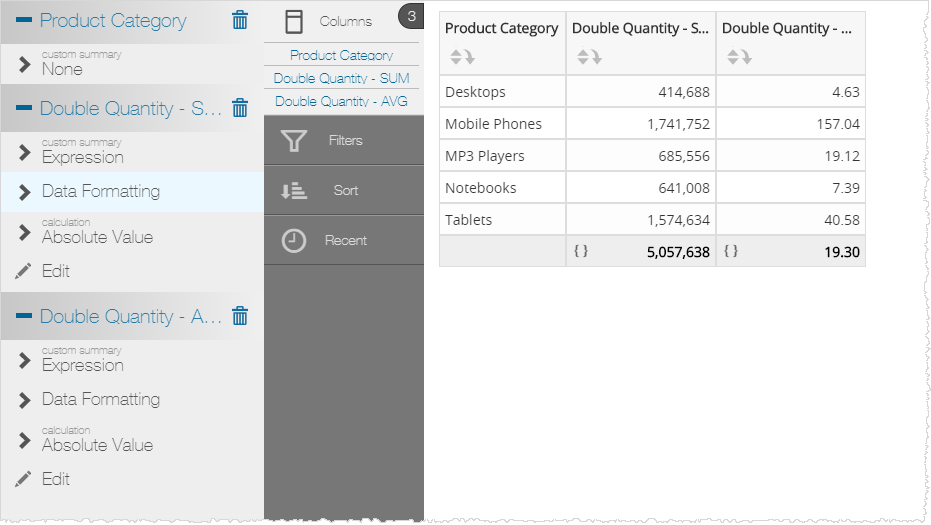
Custom Measure with Aggregate Rule Operator Example
This example shows both a custom measure and the Aggregate Rule operator comparing SUM and AVG.
SUM Expression
SUM([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*2)
AVG Expression
AVG([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*2)
Logical Query
SELECT USING OUTER JOIN AVG([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*2) 'COL0' , SUM([Order_Date: Sum: Quantity]*2) 'COL1' , [Products.Product Category] 'COL2' FROM [ALL]
Results in a Visualizer Report
Custom Measure Based on an Attribute Example
Expression
Sum([Order_Date: Sum: Unit Cost]*[Accounts.Upsell Likelihood])
Logical Query
SELECT USING OUTER JOIN Sum([Order_Date: Sum: Unit Cost]*[Accounts.Upsell Likelihood]) 'COL0' , [Products.Product] 'COL1' FROM [ALL]
Expression in Visualizer
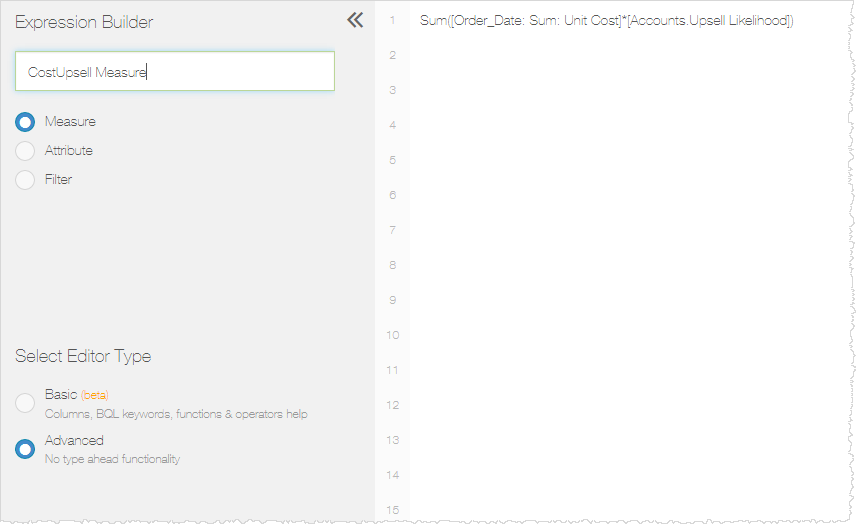
Results in a Visualizer Report